Risk Prediction of Coronary Artery Stenosis in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease Based on Logistic Regression and Artificial Neural Network
- PMID: 35345521
- PMCID: PMC8957440
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3684700
Risk Prediction of Coronary Artery Stenosis in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease Based on Logistic Regression and Artificial Neural Network
Abstract
Objective: Coronary heart disease (CHD) is considered an inflammatory relative disease. This study is aimed at analyzing the health information of serum interferon in CHD based on logistic regression and artificial neural network (ANN) model.
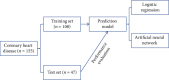
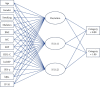
Method: A total of 155 CHD patients diagnosed by coronary angiography in our department from January 2017 to March 2020 were included. All patients were randomly divided into a training set (n = 108) and a test set (n = 47). Logistic regression and ANN models were constructed using the training set data. The predictive factors of coronary artery stenosis were screened, and the predictive effect of the model was evaluated by using the test set data. All the health information of participants was collected. Expressions of serum IFN-γ, MIG, and IP-10 were detected by double antibody sandwich ELISA. Spearman linear correlation analysis determined the relationship between the interferon and degree of stenosis. The logistic regression model was used to evaluate independent risk factors of CHD.
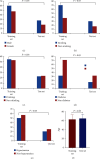
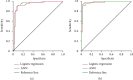
Result: The Spearman correlation analysis showed that the degree of stenosis was positively correlated with serum IFN-γ, MIG, and IP-10 levels. The logistic regression analysis and ANN model showed that the MIG and IP-10 were independent predictors of Gensini score: MIG (95% CI: 0.876~0.934, P < 0.001) and IP-10 (95% CI: 1.009~1.039, P < 0.001). There was no statistically significant difference between the logistic regression and the ANN model (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: The logistic regression model and ANN model have similar predictive performance for coronary artery stenosis risk factors in patients with CHD. In patients with CHD, the expression levels of IFN-γ, IP-10, and MIG are positively correlated with the degree of stenosis. The IP-10 and MIG are independent risk factors for coronary artery stenosis.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaobing Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Uric acid and evaluate the coronary vascular stenosis gensini score correlation research and in gender differences.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Nov 8;23(1):546. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03581-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37940848 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between serum Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) levels and coronary artery stenosis.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023 Jan;33(1):168-176. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2022.10.007. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 36411225
-
[Relationship between serum levels of osteoproteins, inflammatory cytokines and coronary heart disease and disease severity].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 May;31(5):588-593. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.05.013. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31198145 Chinese.
-
sSema4D levels are increased in coronary heart disease and associated with the extent of coronary artery stenosis.Life Sci. 2019 Feb 15;219:329-335. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.01.021. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30658102
-
An artificial neural network prediction model of congenital heart disease based on risk factors: A hospital-based case-control study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Feb;96(6):e6090. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006090. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28178169 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Expression of Serum Ferritin, Human neutrophil lipocalin, Procalcitonin, and inflammatory factors in children with Kawasaki disease and their relationship to coronary artery lesions.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Jan 15;17(1):286-293. doi: 10.62347/MIHQ2583. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39959248 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the risk of acute kidney injury after cardiopulmonary bypass: development and assessment of a new predictive nomogram.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Dec 7;22(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01925-w. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 36476178 Free PMC article.
-
Tongue color parameters in predicting the degree of coronary stenosis: a retrospective cohort study of 282 patients with coronary angiography.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Aug 30;11:1436278. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1436278. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39280030 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors and prediction models for cardiovascular complications of hypertension in older adults with machine learning: A cross-sectional study.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 10;10(6):e27941. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27941. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38509942 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and analysis of artificial neural network diagnosis model for coagulation-related molecular subgroups in coronary artery disease.Front Genet. 2024 Feb 29;15:1351774. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1351774. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38495669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behnamfar N., Zibaeenezhad M. J., Golmoghaddam H., Doroudchi M. d45ro+ memory t-cells produce il-17 in patients with atherosclerosis. Cellular and Molecular Biology (Noisy-le-Grand, France) . 2015;61(8):17–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

