The Value of Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte Ratio for Evaluating Blood Stream Infection Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35345766
- PMCID: PMC8957073
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.832655
The Value of Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte Ratio for Evaluating Blood Stream Infection Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a useful marker of inflammation. However, the prognostic function of the NLR in patients with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) blood stream infection (BSI) remains largely unknown. The aim of this study was to explore the potential relationship between the NLR and mortality in these patients.
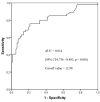
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study based on data retrieved from the computerized patient record system in a tertiary hospital from 1 January 2017 to 31 October, 2020. A total of 134 inpatients with CRKP BSI were enrolled in this study, including 54 fatal cases and 80 survival cases, 28 days after the onset of CRKP BSI. A logistic analysis was performed to assess the association between the NLR on the 4th day and 28-day mortality. Multivariate analyses were used to control for the confounders.
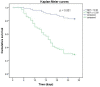
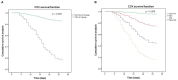
Results: The overall 28-day mortality rate of patients with a CRKP BSI episode was 40.3% (54/134). We conducted a multivariate analysis of the data of 134 patients and found that the NLR on the 4th day [odds ratio (OR) 1.148, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.076-1.225, p < 0.001] and antibiotic exposure before BSI onset (OR 3.847, 95% CI 1.322-11.196, p = 0.013) were independent risk factors for 28-day mortality of patients with CRKP BSI, while appropriate initial therapy (AIT, OR 0.073, 95% CI 0.017-0.307, p < 0.001) was an independent protective factor. Among patients treated with AITs, the Cox proportional hazards regression analysis revealed a significant difference in prognosis (p = 0.006) between the ceftazidime/avibactam contained (CAZ) group and non CAZ-AVI groups. After dividing the non CAZ-AVI group into the tigecycline (TGC), colistin (COL), and TGC + COL groups, there were no differences between the CAZ-AVI group and the TGC group (p = 0.093), but CAZ-AVI group showed lower 28-day mortality than COL (p = 0.002) and TGC + COL (p = 0.002) groups. Meanwhile, there was no difference in NLR on the 1st day (p = 0.958) of patients in different groups but significant difference in NLR on the 4th day (p = 0.047).
Conclusions: The NLR on the 4th day is a readily available and independent prognostic biomarker for patients with CRKP BSI. This marker may have the potential for use in evaluating the efficacy of different anti-infection therapy strategies at an early stage.
Keywords: blood stream infection; carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; prognosis; therapy strategies.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Mao, Du, Zhao, Jiang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ceftazidime-Avibactam-Based Versus Tigecycline-Based Regimen for the Treatment of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae-Induced Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients.Infect Dis Ther. 2021 Dec;10(4):2721-2734. doi: 10.1007/s40121-021-00542-3. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Infect Dis Ther. 2021. PMID: 34652713 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Tertiary Care-Based Cohort Study on Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Ceftazidime-Avibactam-Resistant Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections.Crit Care Res Pract. 2024 Jun 5;2024:3427972. doi: 10.1155/2024/3427972. eCollection 2024. Crit Care Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38868174 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in adult carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection: a retrospective cohort study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Nov 28;14:1461325. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1461325. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39669277 Free PMC article.
-
Ceftazidime/Avibactam-Based Versus Polymyxin B-Based Therapeutic Regimens for the Treatment of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Infect Dis Ther. 2022 Oct;11(5):1917-1934. doi: 10.1007/s40121-022-00682-0. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Infect Dis Ther. 2022. PMID: 35976531 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of ceftazidime-avibactam as definitive treatment for treatment of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 28;11:1118307. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1118307. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36926178 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Retrospective Case-Control Study of Risk Factors for Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Children in China.Pathogens. 2024 Dec 14;13(12):1106. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13121106. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39770365 Free PMC article.
-
Development and application of a nomogram model for the prediction of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in neuro-ICU patients.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0309623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03096-23. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38059625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mosqueda-Gómez JL, Montaño-Loza A, Rolón AL, Cervantes C, Bobadilla-del-Valle JM, Silva-Sánchez J, et al. . Molecular epidemiology and risk factors of bloodstream infections caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae a case-control study. Int J Infect Dis. (2008) 12:653–9. 10.1016/j.ijid.2008.03.008 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

