Effectiveness of single loading dose of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol for deep sedation of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in elderly patients: a prospective randomized study
- PMID: 35346041
- PMCID: PMC8961946
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-022-01630-8
Effectiveness of single loading dose of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol for deep sedation of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in elderly patients: a prospective randomized study
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an advanced endoscopic procedure and requires deep sedation. Deep sedation with dexmedetomidine for the respiratory drive preserved has become popular in recent years. However, the use of dexmedetomidine in elderly patients is controversial because its adverse events are more common. The objective of this study was to investigate the effectiveness of a single loading dose of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol for deep sedation of ERCP in elderly patients.
Methods: In this prospective randomized trial, 49 elderly patients undergoing ERCP were randomly allocated to the dexmedetomidine (DEX) or propofol (PRO) groups. The single loading dose of dexmedetomidine was set at 0.5 μg/kg at the start of anesthesia induction and loading for 10 min. The primary outcome was the cumulative dose of propofol. Secondary outcomes included time to awake, the frequency of airway interventions, and hemodynamics.
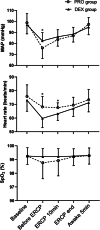
Results: The intraoperative cumulative dose of propofol was lower in the DEX group (111.0 ± 12.6 μg/kg/min) than the PRO group (143.7 ± 23.4 μg/kg/min) (P < 0.001). There was no statistically significant difference in the time to awake between the two groups. The incidence of artificial airway interventions and hypotension in the PRO group (36%, 60%) were significantly higher than those in the DEX group (4.2%, 16.7%) (P = 0.011, P = 0.003, respectively). In addition, the occurrence of bradycardia increased significantly in the DEX group (58.3%) compared with the PRO group (12%) (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The single loading dose of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol can reduce propofol consumption and artificial airway intervention and provide better hemodynamic stability than propofol for deep sedation in elderly patients during ERCP.
Trial registration: www.chictr.org.cn (Registration number ChiCTR1900028069, Registration date 10/12/2019).
Keywords: Deep sedation; Dexmedetomidine; Elderly patients; Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; Propofol.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ikeda Y, Yoshida M, Ishikawa K, Kubo T, Murase K, Takada K, et al. Efficacy of combination therapy with dexmedetomidine for benzodiazepines-induced disinhibition during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2020;13:1756284820911822. doi: 10.1177/1756284820911822. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eberl S, Koers L, van Hooft JE, de Jong E, Schneider T, Hollmann MW, et al. Sedation with propofol during ERCP: is the combination with esketamine more effective and safer than with alfentanil? Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2017;18:472. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2197-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scott-Warren VL, Sebastian J. Dexmedetomidine: its use in intensive care medicine and anaesthesia. BJA Education. 2016;16:242–246. doi: 10.1093/bjaed/mkv047. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical