RIP3 knockdown inhibits necroptosis of human intestinal epithelial cells via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling and ameliorates murine colitis
- PMID: 35346043
- PMCID: PMC8961930
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-022-02208-x
RIP3 knockdown inhibits necroptosis of human intestinal epithelial cells via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling and ameliorates murine colitis
Abstract
Background: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a common inflammatory bowel disease, during which cell necroptosis plays key roles in driving inflammation initiation and aggravation. Previous studies reported Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase 3 (RIP3)-mediated necroptosis in multiple diseases, and RIP3 protein in Paneth cells significantly enriched in the intestines of both humans and mice. Therefore, we hypothesized targeting RIP3 to inhibit necroptosis may depress UC.
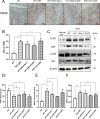
Methods: We classified clinical UC samples according to the modified Truelove & Witts criterion. The expression of RIP3 was measured by western blot and immunohistochemistry. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were analyzed by MTT assay and flow cytometry. ROS production and the secretion of inflammatory cytokines were measured by DCFH-DA probe and ELISA assay. TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway was analyzed by western blot. We established experimental colitis model in RIP3 knockout and wild-type mice and disease activity index (DAI) score was calculated. The expression and distribution of tight junction protein were analyzed by immunofluorescence. The ratio of CD4+Foxp3+ T cells in the spleen was detected by flow cytometry. Oxidative damage of mouse colon was assessed by detecting the levels of SOD, MDA and MPO. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA or student's t test.
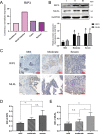
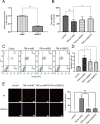
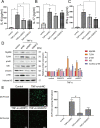
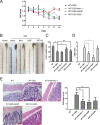
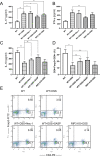
Results: The expression of RIP3 in human colon is positively associated with the severity of UC. RIP3 inhibitor GSK872 or RIP3 knockdown reverses the inhibitory effect of TNF-α on proliferation and the promoting effect of TNF-α on apoptosis and necrosis in human intestinal epithelial cells. In addition, RIP3 deficiency inhibits the secretion of inflammatory cytokines (IL-16, IL-17 and IFN-γ) and ROS production induced by TNF-α. In vivo, RIP3 inhibitor Nec-1 effectively improves DSS-induced colitis in mice. In mechanism, RIP3 depression could upregulate the proportion of CD4+Foxp3+ immunosuppressive Treg cells in the spleen while suppressed TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and ROS generation, and all these anti-inflammation factors together suppress the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and necroptosis of intestinal epithelial cells.
Conclusions: This study preliminarily explored the regulating mechanism of RIP3 on UC, and Nec-1 may be a promising drug to alleviate the inflammation and necroptosis of the colon in UC patients.
Keywords: Nec-1; Necroptosis; Receptor interacting protein kinase 3; TLR4-MyD88; Ulcerative colitis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Xianglian Pill attenuates ulcerative colitis through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;300:115690. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115690. Epub 2022 Sep 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36075274
-
[Effect and mechanism of alkaloids from Portulacae Herba on ulcerative colitis in mice based on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Feb;50(4):874-881. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20241009.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40350807 Chinese.
-
Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through inhibiting of NF-κB signaling pathways and modulating intestinal microbiota.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;298:115640. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115640. Epub 2022 Aug 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36030029
-
Melatonin and necroptosis: therapeutic aspects based on cellular mechanisms.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 17;52(1):606. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10713-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40526280 Review.
-
Pharmacological Effects of Polyphenol Phytochemicals on the Intestinal Inflammation via Targeting TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 22;23(13):6939. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136939. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35805952 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RIP3 in Necroptosis: Underlying Contributions to Traumatic Brain Injury.Neurochem Res. 2024 Feb;49(2):245-257. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04038-z. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37743445 Review.
-
Silencing of TRAF5 enhances necroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting LTBR-mediated NF-κB signaling.PeerJ. 2023 Jun 22;11:e15551. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15551. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37366426 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of HIF1α in intestinal epithelium restricts arthritis inflammation by inhibiting RIPK3-induced cell death machinery.Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Jul 15;83(8):984-997. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224491. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38503474 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoprotein S maintains intestinal homeostasis in ulcerative colitis by inhibiting necroptosis of colonic epithelial cells through modulation of macrophage polarization.Theranostics. 2024 Sep 9;14(15):5903-5925. doi: 10.7150/thno.97005. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39346531 Free PMC article.
-
TGR5 agonist inhibits intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via cAMP/PKA/c-FLIP/JNK signaling pathway and ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Aug;44(8):1649-1664. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01081-y. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36997665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boal Carvalho P, Cotter J. Mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis: a comprehensive review. Drugs. 2017;77(2):159–173. - PubMed
-
- Sun W, Wu X, Gao H, Yu J, Zhao W, Lu JJ, Wang J, Du G, Chen X. Cytosolic calcium mediates RIP1/RIP3 complex-dependent necroptosis through JNK activation and mitochondrial ROS production in human colon cancer cells. Free Radical Biol Med. 2017;108:433–444. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, Wang Y, Zhang Y, He X, Zhong CQ, Ni H, Chen X, Liang Y, Wu J, Zhao S, et al. RIP3 targets pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to increase aerobic respiration in TNF-induced necroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(2):186–197. - PubMed
-
- Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Van Herreweghe F, Vanden Berghe T. The role of the kinases RIP1 and RIP3 in TNF-induced necrosis. Sci Signal. 2010;3(115):re4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

