Late combination of transarterial chemoembolization with apatinib and camrelizumab for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma is superior to early combination
- PMID: 35346114
- PMCID: PMC8961945
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09451-1
Late combination of transarterial chemoembolization with apatinib and camrelizumab for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma is superior to early combination
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to explore the efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with apatinib and camrelizumab (TACE + AC) for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and the impact of the timing of the combination on it.
Methods: In this single-arm retrospective study, consecutive data of patients with unresectable HCC treated to our hospital from March 2017 to September 2021 were collected. These patients were treated with TACE and started on camrelizumab and apatinib within one week of TACE. Camrelizumab 200 mg intravenously once every three weeks and apatinib 250 mg orally once daily. Repeat TACE treatment was available on an on-demand basis. The primary endpoints were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Secondary endpoints included objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and safety. The univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used to assess the effect of early and late combination on OS and PFS.
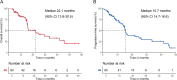
Results: A total of 80 patients were enrolled in this study. The median OS was 22.1 months (95% confidence interval [CI]: 13.8-30.5 months) and the median PFS was 15.7 months (95% CI: 14.7-16.6 months). The ORR was 58.8% (95% CI: 47.2-69.6) and DCR reached 81.2% (95% CI: 71.0-89.1). Multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analyses showed that TACE late combined with apatinib and camrelizumab provided better OS than early combination (HR = 0.175, 95% CI:0.060-0.509, P = 0.001), as did PFS (HR = 0.422, 95% CI:0.184-0.967, P = 0.041). All treatment-related adverse events were tolerable, and no serious adverse events were observed.
Conclusion: TACE combined with apatinib plus camrelizumab for patients with unresectable HCC has promising antitumor activity and a manageable safety profile. For unresectable HCC with large tumor burden, late combination provides better OS and PFS compared to early combination.
Keywords: Apatinib; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Prognosis; Transarterial chemoembolization.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Real-world efficacy and safety of TACE plus camrelizumab and apatinib in patients with HCC (CHANCE2211): a propensity score matching study.Eur Radiol. 2023 Dec;33(12):8669-8681. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09754-2. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37368105 Free PMC article.
-
The addition of camrelizumab is effective and safe among unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients who progress after drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization plus apatinib therapy.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2023 Jan;47(1):102060. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2022.102060. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36473631
-
Efficacy and Safety of the Combination of Transarterial Chemoembolization with Camrelizumab plus Apatinib for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study of 38 Patients from a Single Center.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 May 9;2022:7982118. doi: 10.1155/2022/7982118. eCollection 2022. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35586608 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of camrelizumab combined with TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024 Jan;28(2):687-701. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202401_35066. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38305611
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization combined with targeted therapy and immunotherapy versus with targeted monotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 3;103(18):e38037. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038037. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38701263 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transarterial chemoembolization in combination with programmed death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A mini review.ILIVER. 2022 Nov 4;1(4):225-234. doi: 10.1016/j.iliver.2022.10.001. eCollection 2022 Dec. ILIVER. 2022. PMID: 40636344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with macrovascular invasion or extrahepatic spread: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 54 studies with 6187 hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Jul;72(7):1957-1969. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03390-x. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36811662 Free PMC article.
-
PD-1 inhibitors improve the efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with apatinib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 28;25(1):564. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13932-4. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40155828 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with apatinib with or without PD-1 inhibitors in BCLC stage C hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter retrospective study.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 30;12:961394. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.961394. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36249011 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave ablation and synchronous transarterial chemoembolization combined with PD-1 inhibitor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma following tyrosine kinase inhibitor intolerance.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1097625. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1097625. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36703965 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873917/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No.2020SF004/Science and Technology department of Yibin
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

