Whole-genome sequencing as an investigational device for return of hereditary disease risk and pharmacogenomic results as part of the All of Us Research Program
- PMID: 35346344
- PMCID: PMC8962531
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-022-01031-z
Whole-genome sequencing as an investigational device for return of hereditary disease risk and pharmacogenomic results as part of the All of Us Research Program
Abstract
Background: The All of Us Research Program (AoURP, "the program") is an initiative, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), that aims to enroll one million people (or more) across the USA. Through repeated engagement of participants, a research resource is being created to enable a variety of future observational and interventional studies. The program has also committed to genomic data generation and returning important health-related information to participants.
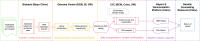
Methods: Whole-genome sequencing (WGS), variant calling processes, data interpretation, and return-of-results procedures had to be created and receive an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The performance of the entire workflow was assessed through the largest known cross-center, WGS-based, validation activity that was refined iteratively through interactions with the FDA over many months.
Results: The accuracy and precision of the WGS process as a device for the return of certain health-related genomic results was determined to be sufficient, and an IDE was granted.
Conclusions: We present here both the process of navigating the IDE application process with the FDA and the results of the validation study as a guide to future projects which may need to follow a similar path. Changes to the program in the future will be covered in supplementary submissions to the IDE and will support additional variant classes, sample types, and any expansion to the reportable regions.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
EV is a cofounder of Codified Genomics. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- The precision medicine initiative cohort program – building a research foundation for 21st century medicine. https://www.nih.gov/sites/default/files/research-training/initiatives/pm.... Accessed 13 May 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

