Iatrogenic dorsal spinal cord herniation and repair with clip-based expansile duraplasty: a case report
- PMID: 35347110
- PMCID: PMC8960805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41394-022-00505-x
Iatrogenic dorsal spinal cord herniation and repair with clip-based expansile duraplasty: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Myelopathy arising due to dorsal herniation of the spinal cord is a rare phenomenon, particularly so in the thoracic region. Where cases of thoracic dorsal cord herniation have been reported, the aetiology has typically been non-iatrogenic.
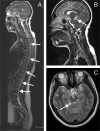
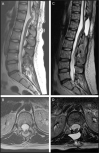
Case presentation: We report the case of a paediatric oncology patient who presented with neurological deterioration secondary to thoracic dorsal spinal cord herniation, manifesting three months after laminectomy for biopsy of a spinal medulloblastoma lesion. We repaired the dural defect using non-penetrating titanium clips to create a secure expansile duraplasty, resulting in radiologically evident reduction of the cord herniation as well as corresponding clinical improvement.
Discussion: Thoracic dorsal spinal cord herniation is an extremely rare occurrence after spinal surgery. Non-penetrating titanium clips can be used to form a secure expansile duraplasty following reduction of the cord herniation. Successful repair of the dural defect re-anteriorises the cord and can confer neurological benefit.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to International Spinal Cord Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest and have no personal, financial or institutional interest in any drugs, materials or devices mentioned or described in this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

