Extracellular matrix-derived and low-cost proteins to improve polyurethane-based scaffolds for vascular grafts
- PMID: 35347181
- PMCID: PMC8960935
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-09040-z
Extracellular matrix-derived and low-cost proteins to improve polyurethane-based scaffolds for vascular grafts
Abstract
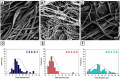
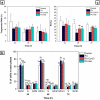
Vascular graft surgeries are often conducted in trauma cases, which has increased the demand for scaffolds with good biocompatibility profiles. Biodegradable scaffolds resembling the extracellular matrix (ECM) of blood vessels are promising vascular graft materials. In the present study, polyurethane (PU) was blended with ECM proteins collagen and elastin (Col-El) and gelatin (Gel) to produce fibrous scaffolds by using the rotary jet spinning (RJS) technique, and their effects on in vitro properties were evaluated. Morphological and structural characterization of the scaffolds was performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). Micrometric fibers with nanometric rugosity were obtained. Col-El and Gel reduced the mechanical strength and increased the hydrophilicity and degradation rates of PU. No platelet adhesion or activation was observed. The addition of proteins to the PU blend increased the viability, adhesion, and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Therefore, PU-Col-El and PU-Gel scaffolds are promising biomaterials for vascular graft applications.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
A novel technique to produce tubular scaffolds based on collagen and elastin.Artif Organs. 2021 May;45(5):E113-E122. doi: 10.1111/aor.13857. Epub 2020 Dec 12. Artif Organs. 2021. PMID: 33169400
-
The preparation and performance of a new polyurethane vascular prosthesis.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013 Jul;66(3):855-66. doi: 10.1007/s12013-013-9528-5. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23456453
-
Biomimetic modification of polyurethane-based nanofibrous vascular grafts: A promising approach towards stable endothelial lining.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017 Nov 1;80:213-221. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.140. Epub 2017 May 29. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 28866159
-
Fabrication of polyurethane and polyurethane based composite fibres by the electrospinning technique for soft tissue engineering of cardiovascular system.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015 Jan;46:166-76. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2014.10.027. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015. PMID: 25491973 Review.
-
State of the Art of Small-Diameter Vessel-Polyurethane Substitutes.Macromol Biosci. 2019 May;19(5):e1800482. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201800482. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Macromol Biosci. 2019. PMID: 30840365 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Fibroblast Differentiation with Electrospun PCL-Zinc Scaffolds Coated with Fibroblast-Derived ECM.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 28;10(5):4427-4441. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07504. eCollection 2025 Feb 11. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39959067 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and characterization of electrospun polycaprolactone/Urechis unicinctus derived-ECM composite scaffolds for small-diameter vascular grafts.RSC Adv. 2025 Aug 29;15(38):31060-31075. doi: 10.1039/d5ra04406e. eCollection 2025 Aug 29. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40896773 Free PMC article.
-
Graphene-Related Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;13(6):1092. doi: 10.3390/nano13061092. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36985986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Magnetically Charged Grafts for Vascular Repair: Process Optimization, Mechanical Characterization and In Vitro Validation.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jul 5;17(13):1877. doi: 10.3390/polym17131877. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Z, Mithieux SM, Weiss AS. Fabrication techniques for vascular and vascularized tissue engineering. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2019;8:1900742. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Chen Z, Yang X. State of the art of small-diameter vessel-polyurethane substitutes. Macromol. Biosci. 2019;19:1800482. - PubMed
-
- Coenen AMJ, Bernaerts KV, Harings JAW, Jockenhoevel S, Ghazanfari S. Elastic materials for tissue engineering applications: Natural, synthetic, and hybrid polymers. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:60–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

