Phrenic Nerve Palsy Following Radiation Therapy for Patient With Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35348081
- PMCID: PMC8784065
- DOI: 10.7812/TPP/20.313
Phrenic Nerve Palsy Following Radiation Therapy for Patient With Breast Cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women in US today. Radiotherapy used after breast-conserving surgery has been shown to decrease local recurrence while minimizing side effects. Peripheral neuropathy remains a common and well-known complication of radiotherapy for breast cancer; however, it is rarely associated with phrenic nerve palsy after treatment of breast cancer.
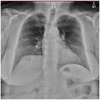
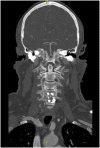
Case presentation: We describe a 66-year-old woman with a significant past medical history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma who presented with hypoxia after completing radiotherapy for breast cancer. After ruling out other causes of hypoxemia, the patient was diagnosed with diaphragmatic dysfunction, likely caused by phrenic nerve palsy resulting from radiotherapy-induced neuropathy after treatment of breast cancer.
Conclusion: This case is the first reported incidence of phrenic nerve palsy resulting from radiotherapy for breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bilateral phrenic nerve dysfunction: a late complication of mantle radiation.J Neurooncol. 2011 Jun;103(2):393-5. doi: 10.1007/s11060-010-0396-1. Epub 2010 Sep 14. J Neurooncol. 2011. PMID: 20838851
-
Phrenic nerve palsy: a rare complication of indwelling subclavian vein catheter.Pediatr Nephrol. 2000 Mar;14(3):203-4. doi: 10.1007/s004670050041. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000. PMID: 10752757
-
Postoperative phrenic nerve palsy: early clinical implications and management.Intensive Care Med. 2006 Aug;32(8):1227-33. doi: 10.1007/s00134-006-0208-4. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Intensive Care Med. 2006. PMID: 16741696
-
Phrenic nerve palsy associated with birth trauma--case reports and a literature review.Brain Dev. 2013 Apr;35(4):363-6. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2012.06.002. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Brain Dev. 2013. PMID: 22742777 Review.
-
Partial unilateral phrenic nerve paralysis caused by a large intrathoracic goitre.Neth J Med. 1996 Jun;48(6):216-9. doi: 10.1016/0300-2977(95)00083-6. Neth J Med. 1996. PMID: 8710041 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (223).Singapore Med J. 2025 Jun 1;66(6):343-347. doi: 10.4103/singaporemedj.SMJ-2023-248. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Singapore Med J. 2025. PMID: 40505106 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Radiation-Induced Unilateral Diaphragmatic Paralysis Following Breast and Nodal Radiotherapy.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2025 Jun 5;12(7):005535. doi: 10.12890/2025_005535. eCollection 2025. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40636227 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous