Head-to-head Intra-individual Comparison of [68Ga]-FAPI and [18F]-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 35349039
- PMCID: PMC9296390
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-022-01715-3
Head-to-head Intra-individual Comparison of [68Ga]-FAPI and [18F]-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Aim/purpose: Fibroblast activation protein-(FAP)-ligands, a novel class of tracers for PET/CT imaging, demonstrated promising results in previous studies in various malignancies compared to standard [18F]FDG PET/CT. 68Ga-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor-([68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI)-PET/CT impresses with sharp contrasts in terms of high tumor uptake and low background noise leading to clear delineation. [18F]FDG PET/CT has limited accuracy in bladder cancer due to high background signal. Therefore, we sought to evaluate the diagnostic potential of [68Ga]FAPI in patients with bladder cancer.
Material and methods: This retrospective analysis consisted of 8 patients (median age 66), 7 of whom underwent both [68Ga]FAPI and [18F]FDG PET/CT scans with a median time interval of 5 days (range 1-20 days). Quantification of tracer uptake was determined with SUVmax and SUVmean. Furthermore, the tumor-to-background ratio (TBR) was derived by dividing the SUVmax of tumor lesions by the SUVmax of adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and blood pool.
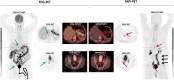
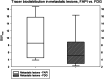
Results: Overall, 31 metastases were detected in five patients including lymph node metastases (n = 23), bone metastases (n = 4), lung metastases (n = 3), and a peritoneal metastasis (n = 1). In one patient, [68Ga]FAPI demonstrated significant uptake in the primary tumor located in the bladder wall. [68Ga]FAPI-PET/CT demonstrated significantly higher uptake compared to [18F]FDG PET/CT with higher mean SUVmax (8.2 vs. 4.6; p = 0.01). Furthermore, [68Ga]FAPI detected additional 30% (n = 9) lesions, missed by [18F]FDG. TBR demonstrated favorable uptake for [68Ga]FAPI in comparison to [18F]FDG. Significant differences were determined with regard to metastasis/blood pool ([68Ga]FAPI 5.3 vs [18F]FDG 1.9; p = 0.001).
Conclusion: [68Ga]FAPI-PET/CT is a promising diagnostic radioligand for patients with bladder cancer. This first described analysis of FAP-ligand in bladder cancer revealed superiority over [18F]FDG in a small patient cohort. Thus, this so far assumed potential has to be confirmed and extended by larger and prospective studies.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; FAPI; Fibroblast activation protein; PET; Urothelial carcinoma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
UH and FLG have a patent application for quinolone based FAP-targeting agents for imaging and therapy in nuclear medicine. UH and FLG also have shares of a consultancy group for iTheranostics. FLG is also advisor at ABX, Telix, and SOFIE Biosciences. SAK reports grants from Viewray Inc. and honoraria from IBA Dosimetry, outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflict of interest regarding this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- IARC, Cancer Today. Estimated number of new cases in 2020, worldwide, both sexes, all ages. 2021 [access date July 2021]. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-table.
-
- Veskimäe E, Espinos EL, Bruins HM et al. What Is the Prognostic and Clinical Importance of Urothelial and Nonurothelial Histological Variants of Bladder Cancer in Predicting Oncological Outcomes in Patients with Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer? A European Association of Urology Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer Guidelines Panel Systematic Review, European Urology Oncology, Volume 2, Issue 6, 2019, Pages 625–642, ISSN 2588–9311. - PubMed
-
- Soubra A, Hayward D, Dahm P, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography in staging bladder cancer: a single-institution study and a systematic review with meta-analysis. World J Urol. 2016;34:1229–1237. doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1772-z. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

