Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibody Therapies in Chronic Autoimmune Demyelinating Neuropathies
- PMID: 35349079
- PMCID: PMC9294114
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-022-01222-x
Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibody Therapies in Chronic Autoimmune Demyelinating Neuropathies
Abstract
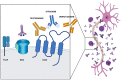
Autoimmune diseases of the peripheral nervous system have so far been treated mainly with exogenous high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg), that act through several mechanisms, including neutralization of pathogenic autoantibodies, modulation of lymphocyte activity, interference with antigen presentation, and interaction with Fc receptors, cytokines, and the complement system. Other therapeutic strategies have recently been developed, in part to address the increasing shortage of IVIg, prime among which is the use of B cell depleting monoclonal antibodies, or small molecule inhibitors targeting the B-cell specific kinases. Rituximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody against CD20 + B lymphocytes, is currently the most used, especially in anti-MAG antibody neuropathy and autoimmune neuropathies with antibodies to nodal/paranodal antigens that are unresponsive to IVIg. After several reports of its efficacy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP), rituximab is currently under investigation in three Phase 2 trials in CIDP. In addition, the possible role of complement activation in the pathogenesis of chronic autoimmune neuropathies has brought into consideration drugs that can block the complement cascade, such as eculizumab, a monoclonal antibody already assessed in acute polyradiculoneuropathies, and approved for myasthenia gravis. Preliminary data on eculizumab in multifocal motor neuropathy have been published, but randomized controlled studies are pending. Moreover, the neonatal Fc receptor, that recycles IgGs by preventing their lysosome degradation, is an important and attractive pharmacological target. Antibodies against FcRn, which reduce circulating IgG (both pathogenic and non-pathogenic) have been developed. The FcRn blocker efgartigimod, a humanized IgG1-derived Fc fragment, which competitively inhibits the FcRn, has recently been approved for the treatment of myasthenia gravis and is currently under investigation in CIDP. In addition, the anti-human FcRn monoclonal antibody rozanolixizumab is currently being assessed in phase 2 trials in CIDP. However, none of the abovementioned monoclonal antibodies is currently approved for treatment of any immune-mediated neuropathies. While more specific and individualized therapies are being developed, the possibility of combined treatments targeting different pathogenic mechanisms deserves consideration as well.
Keywords: Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP); Complement; Eculizumab; Fc receptor; Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN); Neonatal Fc receptor; Nodopathies; Obinutuzumab; Rituximab; anti-MAG antibody neuropathy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Latov N. Immune mechanisms, the role of complement, and related therapies in autoimmune neuropathies. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi N, Misawa S, Sato Y, Nagashima K, Katayama K, Sekiguchi Y, et al. A prospective, multicenter, randomized phase II study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Eeculizumab in patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS): Protocol of Japanese Eculizumab Trial for GBS (JET-GBS). JMIR Res Protoc. 2016;5(4):e210. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

