Anti-CD19 CAR T cells in combination with ibrutinib for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 35349631
- PMCID: PMC9647791
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007317
Anti-CD19 CAR T cells in combination with ibrutinib for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Erratum in
-
Gill S, Vides V, Frey NV, et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cells in combination with ibrutinib for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2022;6(21):5774-5785.Blood Adv. 2023 Nov 14;7(21):6567. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011694. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 37889496 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
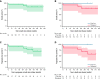
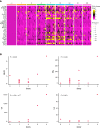
In chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients who achieve a complete remission (CR) to anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CART-19), remissions are remarkably durable. Preclinical data suggesting synergy between CART-19 and the Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib prompted us to conduct a prospective single-center phase 2 trial in which we added autologous anti-CD19 humanized binding domain T cells (huCART-19) to ibrutinib in patients with CLL not in CR despite ≥6 months of ibrutinib. The primary endpoints were safety, feasibility, and achievement of a CR within 3 months. Of 20 enrolled patients, 19 received huCART-19. The median follow-up for all infused patients was 41 months (range, 0.25-58 months). Eighteen patients developed cytokine release syndrome (CRS; grade 1-2 in 15 of 18 subjects), and 5 developed neurotoxicity (grade 1-2 in 4 patients, grade 4 in 1 patient). While the 3-month CR rate among International Working Group on CLL (iwCLL)-evaluable patients was 44% (90% confidence interval [CI], 23-67%), at 12 months, 72% of patients tested had no measurable residual disease (MRD). The estimated overall and progression-free survival at 48 months were 84% and 70%, respectively. Of 15 patients with undetectable MRD at 3 or 6 months, 13 remain in ongoing CR at the last follow-up. In patients with CLL not achieving a CR despite ≥6 months of ibrutinib, adding huCART-19 mediated a high rate of deep and durable remissions. ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02640209.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.G. declares multiple patents related to CAR T cells; is a scientific founder and has equity in Carisma Therapeutics and Interius Biotherapeutics; and reports grants from Carisma Therapeutics and Interius Biotherapeutics. C.H.J. is a scientific founder and has equity in Tmunity Therapeutics and Capstan Therapeutics; reports grants from Tmunity Therapeutics; and is on the scientific advisory boards of BluesphereBio, Cabaletta, Carisma, Cellares, Celldex, ImmuneSensor, Poseida, Verismo, Viracta Therapeutics, WIRB Copernicus Group, and Ziopharm Oncology. J.L.B. is an employee of Novartis Pharmaceuticals. M.V.M. declares multiple patents related to CAR T cells. M.R. declares multiple patents related to CAR T cells. A.R.M. receives research funding from Abbvie and Pharmacyclics and consults for Pharmacyclics. J.C.B. receives honoraria from Novartis and Pharmacyclics; receives research funding from Pharmacyclics; consults for Novartis and Janssen; and has received travel and accommodation expenses from Janssen, Novartis, and Pharacyclics. S.J.S. receives research funding from Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Janssen and consults for Novartis and Pharmacyclics.
D.L.P. is a named inventor on CART-19 related technology. B.L.L. is a consultant for Terumo and GSK; served on the Scientific Advisory Board for Akron, Avectas, Immuneel, Immusoft, In8bio, Ori Biotech, Oxford Biomedica, and Vycellix; and is a cofounder and equity holder in Tmunity Therapeutics and Capstan Therapeutics. Conflict of interest is managed in accordance with University of Pennsylvania policy and oversight. All remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. JULIET Investigators Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45–56. - PubMed
-
- Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396(10254):839–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

