Understanding the complex genetic architecture connecting rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis and inflammation: discovering causal pathways
- PMID: 35349660
- PMCID: PMC9402243
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddac061
Understanding the complex genetic architecture connecting rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis and inflammation: discovering causal pathways
Abstract
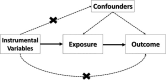
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoporosis (OP) are two comorbid complex inflammatory conditions with evidence of shared genetic background and causal relationships. We aimed to clarify the genetic architecture underlying RA and various OP phenotypes while additionally considering an inflammatory component, C-reactive protein (CRP). Genome-wide association study summary statistics were acquired from the GEnetic Factors for OSteoporosis Consortium, Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research Consortium and UK Biobank. Mendelian randomization (MR) was used to detect the presence of causal relationships. Colocalization analysis was performed to determine shared genetic variants between CRP and OP phenotypes. Analysis of pleiotropy between traits owing to shared causal single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) was performed using PL eiotropic A nalysis under CO mposite null hypothesis (PLACO). MR analysis was suggestive of horizontal pleiotropy between RA and OP traits. RA was a significant causal risk factor for CRP (β = 0.027, 95% confidence interval = 0.016-0.038). There was no evidence of CRP→OP causal relationship, but horizontal pleiotropy was apparent. Colocalization established shared genomic regions between CRP and OP, including GCKR and SERPINA1 genes. Pleiotropy arising from shared causal SNPs revealed through the colocalization analysis was all confirmed by PLACO. These genes were found to be involved in the same molecular function 'protein binding' (GO:0005515) associated with RA, OP and CRP. We identified three major components explaining the epidemiological relationship among RA, OP and inflammation: (1) Pleiotropy explains a portion of the shared genetic relationship between RA and OP, albeit polygenically; (2) RA contributes to CRP elevation and (3) CRP, which is influenced by RA, demonstrated pleiotropy with OP.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights into the pleiotropic relationships between chronic back pain and inflammation-related musculoskeletal conditions: rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporotic abnormalities.Pain. 2023 Mar 1;164(3):e122-e134. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002728. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Pain. 2023. PMID: 36017880
-
Exploring potential shared genetic influences between rheumatoid arthritis and blood lipid levels.Atherosclerosis. 2022 Dec;363:48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.11.006. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Atherosclerosis. 2022. PMID: 36455308
-
Shared Genetic Architecture Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Varying Osteoporotic Phenotypes.J Bone Miner Res. 2022 Mar;37(3):440-453. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4491. Epub 2022 Jan 17. J Bone Miner Res. 2022. PMID: 34910834
-
Analysis of the Relationship between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoporosis Based on Mendelian Randomization.Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2024;20(3):284-295. doi: 10.2174/0115733971261225231021173529. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37937573
-
Analysis of the causal relationship between immune cells and rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of genetic variation: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Adv Rheumatol. 2024 Nov 1;64(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s42358-024-00425-4. Adv Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39487558 Review.
Cited by
-
Mendelian randomization studies of risk and protective factors for osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 16;15:1486188. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1486188. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39886030 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoprotein Acetyls Is a Novel Biomarker Predicting Cardiovascular Complications in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 30;25(11):5981. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115981. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892172 Free PMC article.
-
Association between inflammatory bowel disease and osteoporosis in European and East Asian populations: exploring causality, mediation by nutritional status, and shared genetic architecture.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 29;15:1425610. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425610. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39136019 Free PMC article.
-
A homozygous SP7/OSX mutation causes osteogenesis and dentinogenesis imperfecta with craniofacial anomalies.JBMR Plus. 2024 Mar 4;8(5):ziae026. doi: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziae026. eCollection 2024 May. JBMR Plus. 2024. PMID: 38562913 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Regulators Associated with Osteoporosis: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study.Calcif Tissue Int. 2024 May;114(5):490-501. doi: 10.1007/s00223-024-01200-9. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024. PMID: 38528199
References
-
- Kvien, T.K., Uhlig, T., Ødegård, S. and Heiberg, M.S. (2006) Epidemiological aspects of rheumatoid arthritis: the sex ratio. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1069, 212–222. - PubMed
-
- Doan, T. and Massarotti, E. (2005) Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview of new and emerging therapies. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 45, 751–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous