Cellular Telephone Use and the Risk of Brain Tumors: Update of the UK Million Women Study
- PMID: 35350069
- PMCID: PMC9086806
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djac042
Cellular Telephone Use and the Risk of Brain Tumors: Update of the UK Million Women Study
Abstract
Background: The ongoing debate of whether use of cellular telephones increases the risk of developing a brain tumor was recently fueled by the launch of the fifth generation of wireless technologies. Here, we update follow-up of a large-scale prospective study on the association between cellular telephone use and brain tumors.
Methods: During 1996-2001, 1.3 million women born in 1935-1950 were recruited into the study. Questions on cellular telephone use were first asked in median year 2001 and again in median year 2011. All study participants were followed via record linkage to National Health Services databases on deaths and cancer registrations (including nonmalignant brain tumors).
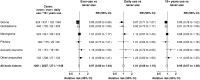
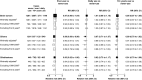
Results: During 14 years follow-up of 776 156 women who completed the 2001 questionnaire, a total of 3268 incident brain tumors were registered. Adjusted relative risks for ever vs never cellular telephone use were 0.97 (95% confidence interval = 0.90 to 1.04) for all brain tumors, 0.89 (95% confidence interval = 0.80 to 0.99) for glioma, and not statistically significantly different to 1.0 for meningioma, pituitary tumors, and acoustic neuroma. Compared with never-users, no statistically significant associations were found, overall or by tumor subtype, for daily cellular telephone use or for having used cellular telephones for at least 10 years. Taking use in 2011 as baseline, there were no statistically significant associations with talking for at least 20 minutes per week or with at least 10 years use. For gliomas occurring in the temporal and parietal lobes, the parts of the brain most likely to be exposed to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields from cellular telephones, relative risks were slightly below 1.0.
Conclusion: Our findings support the accumulating evidence that cellular telephone use under usual conditions does not increase brain tumor incidence.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Comment in
-
Do Cell Phones Cause Brain Tumors? Another Piece of the Puzzle.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022 May 9;114(5):643-644. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djac043. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022. PMID: 35350076 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Hirntumore durch Mobiltelefone?MMW Fortschr Med. 2022 Apr;164(7):10. doi: 10.1007/s15006-022-1056-z. MMW Fortschr Med. 2022. PMID: 35391668 German. No abstract available.
-
RE: Cellular Telephone Use and the Risk of Brain Tumors: Update of the UK Million Women Study.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022 Nov 14;114(11):1551-1552. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djac110. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022. PMID: 35703943 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
RE: Cellular Telephone Use and the Risk of Brain Tumors: Update of the UK Million Women Study.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022 Nov 14;114(11):1549-1550. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djac109. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022. PMID: 35703980 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Handys verursachen keine Hirntumoren.MMW Fortschr Med. 2022 Sep;164(16):28. doi: 10.1007/s15006-022-1930-8. MMW Fortschr Med. 2022. PMID: 36123470 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU). ICT statistics homepage. https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Statistics/Pages/stat/default.aspx. Accessed January 20, 2022.
-
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). Guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020;118(5):483–524. doi:10.1097/HP. 0000000000001210. - PubMed
-
- Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks (SCENIHR). Opinion on Potential Health Effects of Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (EMF). European Commission; 2015. https://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/emerging/docs/scenihr_.... Accessed January 20, 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

