Pak2 Regulation of Nrf2 Serves as a Novel Signaling Nexus Linking ER Stress Response and Oxidative Stress in the Heart
- PMID: 35350536
- PMCID: PMC8957820
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.851419
Pak2 Regulation of Nrf2 Serves as a Novel Signaling Nexus Linking ER Stress Response and Oxidative Stress in the Heart
Abstract
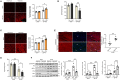
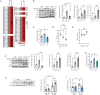
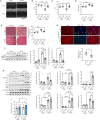
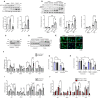
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) stress and oxidative stress have been highly implicated in the pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure (HF). However, the mechanisms involved in the interplay between these processes in the heart are not fully understood. The present study sought to determine a causative link between Pak2-dependent UPR activation and oxidative stress via Nrf2 regulation under pathological ER stress. We report that sustained ER stress and Pak2 deletion in cardiomyocytes enhance Nrf2 expression. Conversely, AAV9 mediated Pak2 delivery in the heart leads to a significant decrease in Nrf2 levels. Pak2 overexpression enhances the XBP1-Hrd1 UPR axis and ameliorates tunicamycin induced cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction in mice. We found that Pak2 deletion and altered proteostasis render Nrf2 detrimental by switching from its antioxidant role to renin-angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) gene regulator. Mechanistically, Pak2 mediated Hrd1 expression targets Nrf2 for ubiquitination and degradation thus preventing its aberrant activation. Moreover, we find a significant increase in Nrf2 with a decrease in Pak2 in human myocardium of dilated heart disease. Using human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs), we find that Pak2 is able to ameliorate Nrf2 induced RAAS activation under ER stress. These findings demonstrate that Pak2 is a novel Nrf2 regulator in the stressed heart. Activation of XBP1-Hrd1 is attributed to prevent ER stress-induced Nrf2 RAAS component upregulation. This mechanism explains the functional dichotomy of Nrf2 in the stressed heart. Thus, Pak2 regulation of Nrf2 homeostasis may present as a potential therapeutic route to alleviate detrimental ER stress and heart failure.
Keywords: ER stress; RAAS and oxidative stress; gene therapy; heart failure; oxidative stress; proteostasis.
Copyright © 2022 Binder, Nguyen, Collins, Zi, Liu, Christou, Luo, Hille, Frey, Cartwright, Chernoff, Müller, Guan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pak2 as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Cardioprotective Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response.Circ Res. 2019 Mar;124(5):696-711. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312829. Circ Res. 2019. PMID: 30620686 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin-Mediated Pak2 Activation Reduces Cardiomyocyte Death Through Suppressing Hypoxia Reoxygenation Injury-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2019 Jul;74(1):20-29. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000678. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31274839
-
Targeting P21-Activated Kinase 2 as a Novel Therapeutic Approach to Mitigate Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Jan 21;14(2):e035302. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.035302. Epub 2025 Jan 10. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 39791428 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and Nrf2 signaling in cardiovascular diseases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):233-242. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.05.027. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26051167 Review.
-
Age-related cataracts: Role of unfolded protein response, Ca2+ mobilization, epigenetic DNA modifications, and loss of Nrf2/Keap1 dependent cytoprotection.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017 Sep;60:1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 28864287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathological implications of cellular stress in cardiovascular diseases.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2023 May;158:106397. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2023.106397. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36931385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ST8Sia2 polysialyltransferase protects against infection by Trypanosoma cruzi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Sep 25;18(9):e0012454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012454. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39321148 Free PMC article.
-
The P21-Activated Kinase 1 and 2 As Potential Therapeutic Targets for the Management of Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Drug Discov Pharm. 2022 Dec 21:5. doi: 10.53941/ijddp.v1i1.179. Online ahead of print. Int J Drug Discov Pharm. 2022. PMID: 39899001 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Vascular Injury and Repair by P21-Activated Kinase 1 and P21-Activated Kinase 2: Therapeutic Potential and Challenges.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 13;14(12):1596. doi: 10.3390/biom14121596. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular diseases in the elderly: possibilities for modulating autophagy using non-coding RNAs.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 31;13:1520850. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1520850. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40823532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frey N, Katus HA, Olson EN, Hill JA. Hypertrophy of the heart. Circulation. (2004) 109:1580–9. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000120390.68287.BB - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- FS/19/39/34447/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/14/71/31063/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/19/66/34600/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/15/16/31477/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/19/70/34650/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/14/70/31039/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/12/76/29852/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/17/31/32988/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/09/052/27833/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/19/53/34499/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/18/73/33973/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

