HDL Composition, Heart Failure, and Its Comorbidities
- PMID: 35350538
- PMCID: PMC8958020
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.846990
HDL Composition, Heart Failure, and Its Comorbidities
Abstract
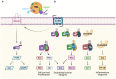
Although research on high-density lipoprotein (HDL) has historically focused on atherosclerotic coronary disease, there exists untapped potential of HDL biology for the treatment of heart failure. Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and endothelial protective properties of HDL could impact heart failure pathogenesis. HDL-associated proteins such as apolipoprotein A-I and M may have significant therapeutic effects on the myocardium, in part by modulating signal transduction pathways and sphingosine-1-phosphate biology. Furthermore, because heart failure is a complex syndrome characterized by multiple comorbidities, there are complex interactions between heart failure, its comorbidities, and lipoprotein homeostatic mechanisms. In this review, we will discuss the effects of heart failure and associated comorbidities on HDL, explore potential cardioprotective properties of HDL, and review novel HDL therapeutic targets in heart failure.
Keywords: apolipoprotein A-I; apolipoprotein M; cardiomyopathy; heart failure; high-density lipoprotein (HDL); sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Copyright © 2022 Diab, Valenzuela Ripoll, Guo and Javaheri.
Conflict of interest statement
AJ has a patent for fusion protein nanodiscs and lipase inhibitors for the treatment of heart failure and has received grant support from AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

