Observed efficacy and clinically important improvements in participants with osteoarthritis treated with subcutaneous tanezumab: results from a 56-week randomized NSAID-controlled study
- PMID: 35351194
- PMCID: PMC8966257
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02759-0
Observed efficacy and clinically important improvements in participants with osteoarthritis treated with subcutaneous tanezumab: results from a 56-week randomized NSAID-controlled study
Abstract
Background: A recent phase 3 study demonstrated that treatment with tanezumab, a nerve growth factor inhibitor, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) improves pain and physical function in participants with moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis (OA) of the hip or knee. Here, we evaluated the time course and clinical importance of these initial efficacy findings using a mixture of primary, secondary, and post hoc endpoints.
Methods: Participants on stable NSAID therapy and with a history of inadequate response to other standard OA analgesics were enrolled in an 80-week (56-week treatment/24-week safety follow-up), randomized, NSAID-controlled, phase 3 study primarily designed to assess the safety of tanezumab for moderate-to-severe OA of the knee or hip. Participants received oral NSAID (twice daily naproxen, celecoxib, or diclofenac) or subcutaneous tanezumab (2.5mg or 5mg every 8 weeks). Non-responders were discontinued at week 16. Changes from baseline in WOMAC Pain and Physical Function, Patient's Global Assessment of Osteoarthritis (PGA-OA), and average pain in the index joint were compared between tanezumab and NSAID groups over the 56-week treatment period. Clinically meaningful response (e.g., ≥30% and ≥50% improvement in WOMAC Pain and Physical Function), rescue medication use, and safety were also assessed.
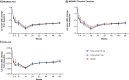
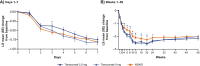
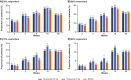
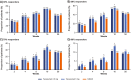
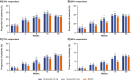
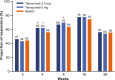
Results: All groups improved WOMAC Pain, WOMAC Physical Function, PGA-OA, and average pain in the index joint over the 56-week treatment period relative to baseline. Across all groups, improvements generally occurred from the time of first assessment (week 1 or 2) to week 16 and then slightly decreased from week 16 to 24 before stabilizing from weeks 24 to 56. The magnitude of improvement and the proportion of participants achieving ≥30% and ≥50% improvement in these measures was greater (unadjusted p≤0.05) with tanezumab than with NSAID at some timepoints on or before week 16. Adverse events of abnormal peripheral sensation, prespecified joint safety events, and total joint replacement surgery occurred more frequently with tanezumab than with NSAID.
Conclusions: Tanezumab and NSAID both provided early and sustained (up to 56 weeks) efficacy relative to baseline. Improvements in pain and function were clinically meaningful in a substantial proportion of participants. Adverse events of abnormal peripheral sensation and joint safety events occurred more frequently with tanezumab than with NSAID.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02528188 . Registered on 19 July 2015.
Keywords: Clinical-trial; Efficacy; Nerve growth factor; Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; Osteoarthritis; Tanezumab.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TN has served as a consultant to Pfizer and Eli Lilly & Company, EMD Merck Serono, Flexion, Novartis, and Regeneron. DJH has served as a consultant to Pfizer, Eli Lilly & Company, Merck Serono, and TLCBio. MC has served on advisory boards for Pfizer and Eli Lilly & Company. IS has no conflicts of interest to disclose. AW has no conflicts of interest to disclose. AG is a shareholder of BICL and LLC and has served as a consultant to MerckSerono, Pfizer, Roche, Galapagos, TissueGene, and AstraZeneca. MO has no conflicts to disclose. LV is a full-time employee of, and owns stocks in, Eli Lilly & Company. RJF, GP, MTB, CRW, and KMV are full-time employees of, and own stock and/or options in, Pfizer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Subcutaneous Tanezumab Versus Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs for Hip or Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Trial.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Jul;73(7):1167-1177. doi: 10.1002/art.41674. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33538113 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of tanezumab monotherapy or combined with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of knee or hip osteoarthritis pain.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jun;74(6):1202-11. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204905. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24625625 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Tanezumab on Joint Pain, Physical Function, and Patient Global Assessment of Osteoarthritis Among Patients With Osteoarthritis of the Hip or Knee: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2019 Jul 2;322(1):37-48. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.8044. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31265100 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of tanezumab administered as a fixed dosing regimen in patients with knee or hip osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled phase III trials.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Jun;40(6):2155-2165. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05488-4. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33159281 Review.
-
Relative Efficacy and Safety of Tanezumab for Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized-Controlled Trials.Clin J Pain. 2021 Dec 1;37(12):914-924. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000986. Clin J Pain. 2021. PMID: 34608021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Controlled Release Strategies for Human Osteoarthritis.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Jan;14(2):e2402737. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202402737. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 39506433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for treatment of musculoskeletal disorders in the past decade].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Mar 20;45(3):661-668. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.24. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40159981 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Efficacy and safety of fasinumab in an NSAID-controlled study in patients with pain due to osteoarthritis of the knee or hip.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Feb 25;26(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08402-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40001000 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Increased nerve growth factor expression and osteoclast density are associated with subchondral bone marrow lesions in osteoarthritic knees.Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2024 Jul 23;6(3):100504. doi: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2024.100504. eCollection 2024 Sep. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2024. PMID: 39176036 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical denervation as a treatment strategy for pain in hand osteoarthritis: a systematic literature review.RMD Open. 2023 Aug;9(3):e003134. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003134. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 37532467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geenen R, Overman CL, Christensen R, Asenlof P, Capela S, Huisinga KL, et al. EULAR recommendations for the health professional’s approach to pain management in inflammatory arthritis and osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:797–807. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons: Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: evidence based guideline 2nd edition. https://aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/osteoarthri.... Accessed 10 Sep 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

