Real-World Effectiveness of Sipuleucel-T on Overall Survival in Men with Advanced Prostate Cancer Treated with Androgen Receptor-Targeting Agents
- PMID: 35352309
- PMCID: PMC9123060
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-022-02085-6
Real-World Effectiveness of Sipuleucel-T on Overall Survival in Men with Advanced Prostate Cancer Treated with Androgen Receptor-Targeting Agents
Abstract
Introduction: The treatment landscape for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) continues to evolve. Sipuleucel-T was the first immunotherapy approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic mCRPC. The androgen receptor-targeting agents (ARTAs) abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide were initially approved to treat mCRPC. Looking at chemotherapy-naïve men with mCRPC, we compared survival outcomes between the sipuleucel-T + ARTA cohort (men who received either sipuleucel-T or an ARTA in the first line, and then the other in the second line within 6 months) and the ARTA monotherapy cohort (men who only received ARTA monotherapy).
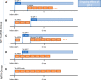
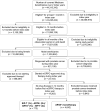
Methods: This retrospective cohort analysis used longitudinal, adjudicated claims data from the US Medicare Fee-for-Service 100% research identifiable dataset that includes both urologic and oncologic practice settings. Eligible men started their first mCRPC treatment with either sipuleucel-T or ARTA in either 2014 or 2015 and had continuous Medicare Parts A, B, and D eligibility for the subsequent 3 years. A multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to analyze overall survival (OS), both overall and by index year, and to control for differences.
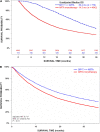
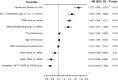
Results: The sipuleucel-T + ARTA and ARTA monotherapy cohorts comprised 773 and 4642 men, respectively, with different characteristics at treatment start. The most commonly used ARTAs were enzalutamide in the former and abiraterone in the latter cohort. Median OS was 30.4 and 14.3 months in the sipuleucel-T + ARTA and ARTA monotherapy cohorts, respectively, with the sipuleucel-T + ARTA cohort having a 28.3% lower risk of death than the ARTA monotherapy cohort (hazard ratio 0.717; 95% CI 0.648, 0.793; p < 0.01).
Conclusions: This real-world study of mCRPC treatment indicates that men receiving sipuleucel-T and ARTAs had a longer median OS than patients receiving treatment with an ARTA alone, suggesting that leveraging mechanisms of action can be beneficial in treating patients with mCRPC.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Observational; Prostate cancer; Real-world evidence; Sequencing; Treatment.
Plain language summary
The treatment landscape for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) continues to evolve. There are multiple treatments for mCRPC, including sipuleucel-T, the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved immunotherapy, and the androgen receptor-targeting agents (ARTAs) abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide. Although sipuleucel-T uses a unique mechanism of action that may be useful in developing a treatment strategy for mCRPC, an optimal treatment algorithm for prostate cancer remains undefined. Therefore, survival was compared in men with mCRPC who received sipuleucel-T and an ARTA in the first 6 months of treatment with those who received only ARTA monotherapy. A retrospective longitudinal study was conducted using the US Medicare Fee-for-Service 100% research identifiable dataset linked to the National Death Index. Eligible men started their first mCRPC treatment with either sipuleucel-T or ARTA in either 2014 or 2015 and had continuous Medicare eligibility for the subsequent 3 years. Men who received treatment with both sipuleucel-T and an ARTA had a longer median survival (30.4 months) than men who received an ARTA without sipuleucel-T (14.3 months). This represents a 28% reduced risk of death with sipuleucel-T. This real-world study of mCRPC treatment indicates that men receiving sipuleucel T and an ARTA survive longer than men who only receive an ARTA, suggesting that changing the mechanism of action can be beneficial in treating patients with mCRPC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Retrospective Observational Analysis of Overall Survival with Sipuleucel-T in Medicare Beneficiaries Treated for Advanced Prostate Cancer.Adv Ther. 2020 Dec;37(12):4910-4929. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01509-5. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 33029725 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of veterans treated with enzalutamide and abiraterone for metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer based on comorbid diseases.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023 Dec;26(4):743-750. doi: 10.1038/s41391-022-00588-5. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023. PMID: 36104504 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world outcomes in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving second-line chemotherapy versus an alternative androgen receptor-targeted agent (ARTA) following early progression on a first-line ARTA in a US community oncology setting.Urol Oncol. 2018 Nov;36(11):500.e1-500.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Urol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30201382
-
Treatment Sequences of Androgen Receptor–Targeted Agents for Prostate Cancer [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2021 Mar. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2021 Mar. PMID: 34260165 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Androgen Receptor Targeted Agents for Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2019 Jun 6. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2019 Jun 6. PMID: 31449370 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
The Immune Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Review.Oncology. 2025;103(6):521-545. doi: 10.1159/000541881. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Oncology. 2025. PMID: 39380471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to 19F MRI: applications, technique, and getting started.BJR Open. 2023 Sep 29;5(1):20230019. doi: 10.1259/bjro.20230019. eCollection 2023. BJR Open. 2023. PMID: 37953866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy in Prostate Cancer: State of Art and New Therapeutic Perspectives.Curr Oncol. 2023 Jun 13;30(6):5769-5794. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30060432. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37366915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming Prostate Cancer Care: Innovations in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 4;26(11):5386. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115386. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in bio-immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(14):13451-13458. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05152-9. Epub 2023 Jul 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37460807 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Prostate Cancer: version 1.2022. 2021 [NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology]. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate.pdf. Accessed Sept 14, 2021.
-
- Flanders S, Lowentritt BH, Mezzio D, Friedman M, Moses K. Abstract C28: Estimating adverse drug event (ADE) costs associated with treatments in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2020;26(4-a Suppl):S17.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

