Characterization of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in cats with naturally occurring chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 35352404
- PMCID: PMC8965263
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.16361
Characterization of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in cats with naturally occurring chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: The role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is incompletely understood.
Objective: To characterize components of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in cats with CKD.
Animals: Eleven cats with naturally occurring CKD (CKD group) and 8 healthy control cats.
Methods: Renal tissue samples were evaluated by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction for renin, angiotensinogen, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), and angiotensin II type 1 receptor transcript levels, and by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for quantification of angiotensin I, II, III, and IV concentrations. Linear mixed models were used to compare gene transcript levels and concentrations of angiotensin peptides between groups.
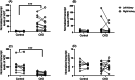
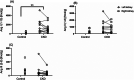
Results: Cats of the CKD group were significantly older (P < .001) and more likely to be neutered (P = .007) than healthy control cats. Kidneys from cats with CKD had significantly higher transcript levels of angiotensinogen (P < .001) and lower transcript levels of ACE (P < .001) than those from control cats. Renal angiotensin I concentrations were increased in CKD compared with control kidneys (P = .001). No other significant differences in renal transcript levels or angiotensin peptide concentrations were noted between groups.
Conclusion and clinical importance: The intrarenal RAS might be activated in cats with CKD. Small sample size and differences in age, neuter status, and dietary sodium intake between groups might have limited the ability to identify a significant difference in concentration of renal angiotensin II.
Keywords: angiotensin-converting enzyme; angiotensinogen; equilibrium analysis; tissular RAAS.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Bianca Lourenço was the recipient of a Boehringer Ingelheim Postdoctoral Scholarship. No other authors have a conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Post hoc comparison of the intrarenal and circulating renin-angiotensin(-aldosterone) systems in cats with ischemia-induced chronic kidney disease.Physiol Rep. 2025 Jun;13(12):e70417. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70417. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40560995 Free PMC article.
-
Intrarenal distributions and changes of Angiotensin-converting enzyme and Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in feline and canine chronic kidney disease.J Vet Med Sci. 2014 Jan;76(1):45-50. doi: 10.1292/jvms.13-0314. Epub 2013 Sep 5. J Vet Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24004970 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system and renal injury in chronic kidney disease of dogs and cats.J Vet Med Sci. 2013 Feb;75(2):127-33. doi: 10.1292/jvms.12-0314. Epub 2012 Sep 14. J Vet Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 22986274
-
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in kidney diseases of cats and dogs.Vet J. 2025 Feb;309:106287. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2024.106287. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Vet J. 2025. PMID: 39672318 Review.
-
Augmented intrarenal and urinary angiotensinogen in hypertension and chronic kidney disease.Pflugers Arch. 2013 Jan;465(1):3-12. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1143-6. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 22918624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post hoc comparison of the intrarenal and circulating renin-angiotensin(-aldosterone) systems in cats with ischemia-induced chronic kidney disease.Physiol Rep. 2025 Jun;13(12):e70417. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70417. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40560995 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Components and Enzymes in Systemically Hypertensive Cats Receiving Amlodipine.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 10;13(22):3479. doi: 10.3390/ani13223479. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003097 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial and Renal Renin-Angiotensin System Enzyme Activity in Dogs.J Vet Intern Med. 2025 Jul-Aug;39(4):e70181. doi: 10.1111/jvim.70181. J Vet Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40601867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peach MJ. Renin‐angiotensin system: biochemistry and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev. 1977;57:313‐370. - PubMed
-
- De Gasparo M, Catt K, Inagami T, et al. International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:415‐472. - PubMed
-
- Brewster UC, Perazella MA. The renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system and the kidney: effects on kidney disease. Am J Med. 2004;116:263‐272. - PubMed
-
- Ruster C, Wolf G. Angiotensin II as a morphogenic cytokine stimulating renal fibrogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:1189‐1199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

