Strategies to Improve the Potency of Oxazolidinones towards Bacterial Biofilms
- PMID: 35352479
- PMCID: PMC9321984
- DOI: 10.1002/asia.202200201
Strategies to Improve the Potency of Oxazolidinones towards Bacterial Biofilms
Abstract
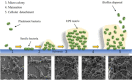
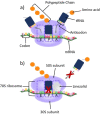
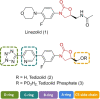
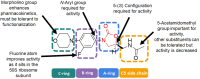
Biofilms are part of the natural lifecycle of bacteria and are known to cause chronic infections that are difficult to treat. Most antibiotics are developed and tested against bacteria in the planktonic state and are ineffective against bacterial biofilms. The oxazolidinones, including the last resort drug linezolid, are one of the main classes of synthetic antibiotics progressed to clinical use in the last 50 years. They have a unique mechanism of action and only develop low levels of resistance in the clinical setting. With the aim of providing insight into strategies to design more potent antibiotic compounds with activity against bacterial biofilms, we review the biofilm activity of clinically approved oxazolidinones and report on structural modifications to oxazolidinones and their delivery systems which lead to enhanced anti-biofilm activity.
Keywords: Antibiotics; Biofilm; Drug Design; Drug delivery; Oxazolidinone.
© 2022 The Authors. Chemistry - An Asian Journal published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
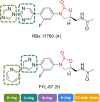
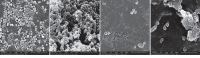
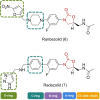
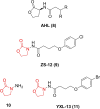
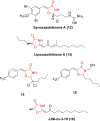
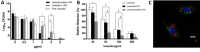
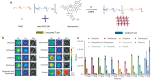
References
-
- Martens E., Demain A. L., J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 520–526. - PubMed
-
- Costerton J. W., Stewart Philip S., Greenberg E. P., Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. - PubMed
-
- Wolcott R. D., Rhoads D. D., Bennett M. E., Wolcott B. M., Gogokhia L., Costerton J. W., Dowd S. E., J. Wound Care 2010, 19, 45–53. - PubMed
-
- Römling U., Balsalobre C., J. Intern. Med. 2012, 272, 541–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

