Associations between cardiometabolic disease severity, social determinants of health (SDoH), and poor COVID-19 outcomes
- PMID: 35352489
- PMCID: PMC9088642
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.23440
Associations between cardiometabolic disease severity, social determinants of health (SDoH), and poor COVID-19 outcomes
Abstract
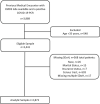
Objective: This study aimed to determine the ability of retrospective cardiometabolic disease staging (CMDS) and social determinants of health (SDoH) to predict COVID-19 outcomes.
Methods: Individual and neighborhood SDoH and CMDS clinical parameters (BMI, glucose, blood pressure, high-density lipoprotein, triglycerides), collected up to 3 years prior to a positive COVID-19 test, were extracted from the electronic medical record. Bayesian logistic regression was used to model CMDS and SDoH to predict subsequent hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and mortality, and whether adding SDoH to the CMDS model improved prediction was investigated. Models were cross validated, and areas under the curve (AUC) were compared.
Results: A total of 2,873 patients were identified (mean age: 58 years [SD 13.2], 59% were female, 45% were Black). CMDS, insurance status, male sex, and higher glucose values were associated with increased odds of all outcomes; area-level social vulnerability was associated with increased odds of hospitalization (odds ratio: 1.84, 95% CI: 1.38-2.45) and ICU admission (odds ratio 1.98, 95% CI: 1.45-2.85). The AUCs improved when SDoH were added to CMDS (p < 0.001): hospitalization (AUC 0.78 vs. 0.82), ICU admission (AUC 0.77 vs. 0.81), and mortality (AUC 0.77 vs. 0.83).
Conclusions: Retrospective clinical markers of cardiometabolic disease and SDoH were independently predictive of COVID-19 outcomes in the population.
© 2022 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adding social determinants of health to the equation: Development of a cardiometabolic disease staging model using clinical and social determinants of health to predict type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 May;27(5):2454-2462. doi: 10.1111/dom.16241. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39927418 Free PMC article.
-
Race Versus Social Determinants of Health in COVID-19 Hospitalization Prediction.Am J Prev Med. 2022 Jul;63(1 Suppl 1):S103-S108. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2022.01.034. Am J Prev Med. 2022. PMID: 35725136 Free PMC article.
-
Social Determinants of Health and Limitation of Life-Sustaining Therapy in Neurocritical Care: A CHoRUS Pilot Project.Neurocrit Care. 2024 Dec;41(3):866-879. doi: 10.1007/s12028-024-02007-0. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Neurocrit Care. 2024. PMID: 38844599
-
The social determinants of health associated with cardiometabolic diseases among Asian American subgroups: a systematic review.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Feb 25;22(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-07646-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 35216607 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Social Determinants of Health and Prostate Cancer Outcomes Among Black and White Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jan 3;6(1):e2250416. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.50416. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 36630135 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Patients with unmet social needs are at higher risks of developing severe long COVID-19 symptoms and neuropsychiatric sequela.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 2;14(1):7743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58430-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38565574 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in COVID-19-Related Hospitalization, Treatment, Complications, and Death by Race and Ethnicity and Area-Level Measures Among Individuals with Cancer in the ASCO Registry.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 2;17(5):857. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050857. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075704 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and Overweight: Probing Causes, Consequences, and Novel Therapeutic Approaches Through the American Heart Association's Strategically Focused Research Network.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Feb 21;12(4):e027693. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.027693. Epub 2023 Feb 8. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36752232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adding social determinants of health to the equation: Development of a cardiometabolic disease staging model using clinical and social determinants of health to predict type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 May;27(5):2454-2462. doi: 10.1111/dom.16241. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39927418 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of patients with pre-existing coronary artery disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection.EBioMedicine. 2025 Jun;116:105778. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105778. Epub 2025 May 28. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40440913 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

