Effect of the p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Cascade on Radiation Biodosimetry
- PMID: 35353886
- PMCID: PMC9310339
- DOI: 10.1667/RADE-21-00240.1
Effect of the p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Cascade on Radiation Biodosimetry
Abstract
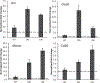
Radiation biodosimetry based on transcriptomic analysis of peripheral blood is a valuable tool to detect radiation exposure after a radiological/nuclear event and obtain useful biological information that could predict tissue and organismal injury. However, confounding factors, including chronic inflammation or immune suppression, can potentially obscure the predictive power of the method. Members of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family respond to pro-inflammatory signals and environmental stresses, whereas genetic ablation of the p38 signaling pathway in mice leads to reduced susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis that model human rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, respectively. p38 is normally regulated by the MAP3K-MAP2K pathway in mammalian cells. However, in T cells there is an alternative pathway for p38 activation that plays an important role in antigen-receptor-activated T cells and participates in immune and inflammatory responses. To examine the role of p38 in response to radiation, we used two mouse models expressing either a p38α dominant negative (DN) mutation that globally suppresses p38 signaling or a p38αβ double-knock-in (DKI) mutant, which inhibits specifically T-cell receptor activation. We exposed p38 wild-type (p38WT) and mutant male mice to 7 Gy X rays and 24 h later whole blood was isolated subjected to whole-genome microarray and gene ontology analysis. Irradiation of p38WT mice led to a significant overrepresentation of pathways associated with morbidity and mortality, as well as organismal cell death. In contrast, these pathways were significantly underrepresented in p38DN and p38DKI mutant mice, suggesting that p38 attenuation may protect blood cells from the deleterious effects of radiation. Furthermore, radiation exposure in p38 mutant mice resulted in an enrichment of phagocytosis-related pathways, suggesting a role for p38 signaling in restricting phagocytosis of apoptotic cells after irradiation. Finally, despite the significant changes in gene expression, it was still feasible to identify a panel of genes that could accurately distinguish between irradiated and control mice, irrespective of p38 status.
©2022 by Radiation Research Society. All rights of reproduction in any form reserved.
Figures

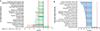


Similar articles
-
Impact of GADD45A on Radiation Biodosimetry Using Mouse Peripheral Blood.Radiat Res. 2023 Sep 1;200(3):296-306. doi: 10.1667/RADE-23-00052.1. Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 37421415 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite effects of Ha-Ras and Ki-Ras on radiation-induced apoptosis via differential activation of PI3K/Akt and Rac/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.Oncogene. 2004 Jan 8;23(1):9-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206982. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 14712206
-
Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by PYK2/related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase-dependent mechanism.J Biol Chem. 1999 Apr 9;274(15):10140-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.15.10140. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10187797
-
p38 pathway kinases as anti-inflammatory drug targets.J Dent Res. 2007 Sep;86(9):800-11. doi: 10.1177/154405910708600902. J Dent Res. 2007. PMID: 17720847 Review.
-
Stress and radiation-induced activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways.Radiat Res. 2003 Mar;159(3):283-300. doi: 10.1667/0033-7587(2003)159[0283:sariao]2.0.co;2. Radiat Res. 2003. PMID: 12600231 Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-platform validation of a mouse blood gene signature for quantitative reconstruction of radiation dose.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 19;12(1):14124. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18558-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35986207 Free PMC article.
-
Host microbiome depletion attenuates biofluid metabolite responses following radiation exposure.PLoS One. 2024 May 17;19(5):e0300883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300883. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38758927 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of High-Linear-Energy-Transfer Heavy Ion Radiation on Intestinal Stem Cells: Implications for Gut Health and Tumorigenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 4;16(19):3392. doi: 10.3390/cancers16193392. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39410012 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of GADD45A on Radiation Biodosimetry Using Mouse Peripheral Blood.Radiat Res. 2023 Sep 1;200(3):296-306. doi: 10.1667/RADE-23-00052.1. Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 37421415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashwell JD. The many paths to p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006; 6:532–40. - PubMed
-
- Hale KK, Trollinger D, Rihanek M, Manthey CL. Differential expression and activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase alpha, beta, gamma, and delta in inflammatory cell lineages. J Immunol. 1999; 162:4246–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

