Thiol redox switches regulate the oligomeric state of cyanobacterial Rre1, RpaA and RpaB response regulators
- PMID: 35353903
- PMCID: PMC9321951
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14340
Thiol redox switches regulate the oligomeric state of cyanobacterial Rre1, RpaA and RpaB response regulators
Abstract
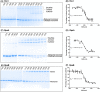
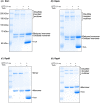
Cyanobacteria employ two-component sensor-response regulator systems to monitor and respond to environmental challenges. The response regulators RpaA, RpaB, Rre1 and RppA are integral to circadian clock function and abiotic stress acclimation in cyanobacteria. RpaA, RpaB and Rre1 are known to interact with ferredoxin or thioredoxin, raising the possibility of their thiol regulation. Here, we report that Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 Rre1, RpaA and RpaB exist as higher-order oligomers under oxidising conditions and that reduced thioredoxin A converts them to monomers. We further show that these response regulators contain redox-responsive cysteine residues with an Em7 around -300 mV. These findings suggest a direct thiol modulation of the activity of these response regulators, independent of their cognate sensor kinases.
Keywords: Hik2; RpaA; RpaB; Rre1; TrxA; thiol regulation.
© 2022 The Authors. FEBS Letters published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mary I, Vaulot D. Two‐component systems in Prochlorococcus MED4: genomic analysis and differential expression under stress. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003;226:135–44. - PubMed
-
- Ashby MK, Mullineaux CW. Cyanobacterial ycf27 gene products regulate energy transfer from phycobilisomes to photosystems I and II. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;181:253–60. - PubMed
-
- Laub MT, Goulian M. Specificity in two‐component signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Genet. 2007;41:121–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

