Comparing Drugs for Out-of-hospital, Shock-refractory Cardiac Arrest: Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 35354019
- PMCID: PMC8328185
- DOI: 10.5811/westjem.2021.2.49590
Comparing Drugs for Out-of-hospital, Shock-refractory Cardiac Arrest: Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Introduction: The benefit of medications used in out-of-hospital, shock-refractory cardiac arrest remains controversial. This study aims to compare the treatment outcomes of medications for out-of-hospital, shock-refractory ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT).
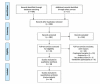
Methods: The inclusion criteria were randomized controlled trials of participants older than eight years old who had atraumatic, out-of-hospital, shock-refractory VF/pVT in which at least one studied group received a medication. We conducted a database search on October 28, 2019, that included PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL Complete, and Cochrane CENTRAL. Citations of relevant meta-analyses were also searched. We performed frequentist network meta-analysis (NMA) to combine the comparisons. The outcomes were analyzed by using odds ratios (OR) and compared to placebo. The primary outcome was survival to hospital discharge. The secondary outcomes included the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), survival to hospital admission, and the neurological outcome at discharge. We ranked all outcomes using surface under the cumulative ranking score.
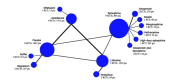
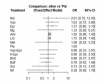
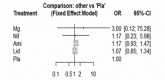
Results: We included 18 studies with 6,582 participants. The NMA of 20 comparisons included 12 medications and placebo. Only norepinephrine showed a significant increase of ROSC (OR = 8.91, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.88-42.29). Amiodarone significantly improved survival to hospital admission (OR = 1.53, 95% CI, 1.01-2.32). The ROSC and survival-to-hospital admission data were significantly heterogeneous with the I2 of 55.1% and 59.1%, respectively. This NMA satisfied the assumption of transitivity.
Conclusion: No medication was associated with improved survival to hospital discharge from out-of-hospital, shock-refractory cardiac arrest. For the secondary outcomes, norepinephrine was associated with improved ROSC and amiodarone was associated with an increased likelihood of survival to hospital admission in the NMA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous chest compression versus interrupted chest compression for cardiopulmonary resuscitation of non-asphyxial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 27;3(3):CD010134. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010134.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28349529 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
Cited by
-
First Results of Our Local Practice Guide Used During the Late Phase of Resuscitation in Patients with Refractory VF in Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest.Open Access Emerg Med. 2025 May 28;17:203-213. doi: 10.2147/OAEM.S510483. eCollection 2025. Open Access Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40453369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berdowski J, Berg RA, Tijssen JGP, et al. Global incidences of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and survival rates: systematic review of 67 prospective studies. Resuscitation. 2010;81(11):1479–87. - PubMed
-
- Kragholm K, Wissenberg M, Mortensen RN, et al. Bystander efforts and 1-year outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(18):1737–47. - PubMed
-
- Link MS, Berkow LC, Kudenchuk PJ, et al. Part 7: Adult advanced cardiovascular life support. Circulation. 2015;132(18_suppl_2):S444–64. - PubMed
-
- Panchal AR, Berg KM, Kudenchuk PJ, et al. 2018 American Heart Association focused update on advanced cardiovascular life support use of antiarrhythmic drugs during and immediately after cardiac arrest: an update to the American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2018;138(23):e740–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belletti A, Benedetto U, Putzu A, et al. Vasopressors during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. A network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(5):e443–51. - PubMed
