Developmental coupling of cerebral blood flow and fMRI fluctuations in youth
- PMID: 35354053
- PMCID: PMC9006592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110576
Developmental coupling of cerebral blood flow and fMRI fluctuations in youth
Abstract
The functions of the human brain are metabolically expensive and reliant on coupling between cerebral blood flow (CBF) and neural activity, yet how this coupling evolves over development remains unexplored. Here, we examine the relationship between CBF, measured by arterial spin labeling, and the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) from resting-state magnetic resonance imaging across a sample of 831 children (478 females, aged 8-22 years) from the Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort. We first use locally weighted regressions on the cortical surface to quantify CBF-ALFF coupling. We relate coupling to age, sex, and executive functioning with generalized additive models and assess network enrichment via spin testing. We demonstrate regionally specific changes in coupling over age and show that variations in coupling are related to biological sex and executive function. Our results highlight the importance of CBF-ALFF coupling throughout development; we discuss its potential as a future target for the study of neuropsychiatric diseases.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; adolescence; amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations; cerebral blood flow; development; executive function; frontoparietal; neurovascular coupling; sex differences.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors have no competing interests.
Figures

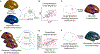
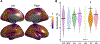

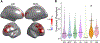

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RF1 MH121867/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH125829/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH123550/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089924/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113550/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH014654/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH123063/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH120174/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089983/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH019112/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB022573/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH112847/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107235/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH120482/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG066656/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH119185/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

