Treatment of Large Cartilage Defects in the Knee by Hydrogel-Based Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation: Two-Year Results of a Prospective, Multicenter, Single-Arm Phase III Trial
- PMID: 35354310
- PMCID: PMC9137299
- DOI: 10.1177/19476035221085146
Treatment of Large Cartilage Defects in the Knee by Hydrogel-Based Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation: Two-Year Results of a Prospective, Multicenter, Single-Arm Phase III Trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the clinical outcome of a hydrogel-based autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) for large articular cartilage defects in the knee joint.
Design: Prospective, multicenter, single-arm, phase III clinical trial. ACI was performed in 100 patients with focal full-thickness cartilage defects ranging from 4 to 12 cm2 in size. The primary outcome measure was the responder rate at 2 years using the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS).
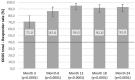
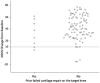
Results: Two years after ACI treatment, 93% of patients were KOOS responders having improved by ≥10 points compared with their pre-operative level. The primary endpoint of the study was met and demonstrated that the KOOS response rate is markedly greater than 40% with a lower 95% CI (confidence interval) of 86.1, more than twice the pre-specified no-effect level. KOOS improvement (least squares mean) was 42.0 ± 1.8 points (95% CI between 38.4 and 45.7). Mean changes from baseline were significant in the overall KOOS and in all 5 KOOS subscores from Month 3 (first measurement) to Month 24 (inclusive) (P < 0.0001). The mean MOCART (Magnetic Resonance Observation of Cartilage Repair Tissue) score after 24 months reached 80.0 points (95% CI: 70.0-90.0 points) and 92.1 points in lesions ≤ 5 cm2.
Conclusions: Overall, hydrogel-based ACI proved to be a valuable treatment option for patients with large cartilage defects in the knee as demonstrated by early, statistically significant, and clinically meaningful improvement up to 2 years follow-up. Parallel to the clinical improvements, MRI analyses suggested increasing maturation, re-organization, and integration of the repair tissue.
Trial registration: NCT03319797; EudraCT No.: 2016-002817-22.
Keywords: autologous chondrocyte implantation; cartilage repair; hydrogel; knee; large defects.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Heir S, Nerhus TK, Rotterud JH, Løken S, Ekeland A, Engebretsen L, et al.. Focal cartilage defects in the knee impair quality of life as much as severe osteoarthritis: a comparison of Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score in 4 patient categories scheduled for knee surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(2):231-7. doi:10.1177/0363546509352157. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Everhart JS, Abouljoud MM, Kirven JC, Flanigan DC. Full-thickness cartilage defects are important independent predictive factors for progression to total knee arthroplasty in older adults with minimal to moderate osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(1):56-63. doi:10.2106/JBJS.17.01657. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Niemeyer P, Albrecht D, Andereya S, Angele P, Ateschrang A, Aurich M, et al.. Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) for cartilage defects of the knee: a guideline by the working group “Clinical Tissue Regeneration” of the German Society of Orthopaedics and Trauma (DGOU). Knee. 2016;23(3):426-35. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2016.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khella CM, Asgarian R, Horvath JM, Rolauffs B, Hart ML. An evidence-based systematic review of human knee post-traumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA): timeline of clinical presentation and disease markers, comparison of knee joint PTOA models and early disease implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1996. doi:10.3390/ijms22041996. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

