Effect of phenyllactic acid on silage fermentation and bacterial community of reed canary grass on the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau
- PMID: 35354370
- PMCID: PMC8966296
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-022-02499-w
Effect of phenyllactic acid on silage fermentation and bacterial community of reed canary grass on the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the effect of phenyllactic acid as an additive on silage fermentation and bacterial community of reed canary grass (RCG, Phalaris arundinacea L.) on the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. At the heading stage, RCG was harvested, chopped and ensiled in small bag silos. The silage was treated without (control, 1.0 g/mL sterile water, on a fresh matter basis (FM)) or with phenyllactic acid (PLA, 3 mg/mL, FM), antimicrobial additive (PSB, a mixture of potassium sorbate and sodium benzoate, 2%, FM), lactic acid bacteria inoculant (LABi, L. plantarum + L. curvatus, 1 × 106 cfu/g, FM) and PLA + LABi, and then stored in a dark room at the ambient temperature (5 ~ 15 °C) for 60 days.
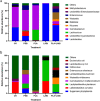
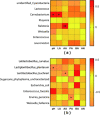
Results: Compared with control, PLA decreased lactic acid, acetic acid and ammonia-N contents, and subsequently increased CP content of RCG silage. PLA enhanced the growth of lactic acid bacteria and reduced the count of yeasts (P < 0.05) in RCG silage, with reduced bacterial richness index (Chao1), observed operational taxonomic units and diversity index (Simpson). In relative to control, moreover, PLA and PLA + LABi increased the relative abundance of Lactococcus in RCG silage by 27.73 and 16.93%, respectively.
Conclusions: Therefore, phenyllactic acid at ensiling improved nutritional quality of RCG silage by advancing the disappearance of yeasts and the dominance of Lactococcus.
Keywords: Bacterial population; Bioactive agents; Ensilage; Fermentation quality; Phalaris arundinacea.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inoculation of exogenous lactic acid bacteria exerted a limited influence on the silage fermentation and bacterial community compositions of reed canary grass straw on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Nov;129(5):1163-1172. doi: 10.1111/jam.14698. Epub 2020 May 26. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32392369
-
Effects of inoculants on the fermentation characteristics and in vitro digestibility of reed canary grass (Phalaris arundinacea L.) silage on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau.Anim Sci J. 2020 Jan-Dec;91(1):e13364. doi: 10.1111/asj.13364. Anim Sci J. 2020. PMID: 32219952
-
Effects of maturity stage and lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of Siberian wildrye silage.Food Sci Nutr. 2016 Jun 21;4(5):664-70. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.312. eCollection 2016 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27625768 Free PMC article.
-
Redefining methods for augmenting lactic acid bacteria robustness and phenyllactic acid biocatalysis: Integration valorizes simplicity.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(13):4397-4409. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2141681. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36322699 Review.
-
Recent development of phenyllactic acid: physicochemical properties, biotechnological production strategies and applications.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2023 Mar;43(2):293-308. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.2010645. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 34965820 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutrition, Flavor, and Microbial Communities of Two Traditional Bacterial Douchi from Gansu, China.Foods. 2024 Nov 4;13(21):3519. doi: 10.3390/foods13213519. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39517303 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Lactiplantibacillus and sea buckthorn pomace on the fermentation quality and microbial community of paper mulberry silage.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 30;15:1412759. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1412759. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39280944 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Isolated LAB on Chemical Composition, Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Stipa grandis Silage.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 13;10(12):2463. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122463. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557716 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of isolated lactic acid bacteria on the quality and bacterial diversity of native grass silage.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jul 6;14:1160369. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1160369. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37484462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou J, Liu H, Zhong C. Apparent digestibility, rumen fermentation, digestive enzymes and urinary purine derivatives in yaks and Qaidam cattle offered forage-concentrate diets with different nitrogen concentration. Livest Sci. 2018;208:14–21. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2017.11.020. - DOI
-
- Zhong J, Zhijie M, Zhixin C, Hui W, Zhang C, Qiumei J, Jinwei X. Whole genome sequencing of the dzo: genetic implications for high-altitude adaptation, sterility, and milk and meat production. Kafkas Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi. 2018;24(6):835–844. doi: 10.9775/kvfd.2018.20022. - DOI
-
- Wilkinson JM, Rinne M. Highlights of progress in silage conservation and future perspectives. Grass Forage Sci. 2018;73(1):40–52. doi: 10.1111/gfs.12327. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

