Analysis of lung cancer-related genetic changes in long-term and low-dose polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate (PHMG-p) treated human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells
- PMID: 35354498
- PMCID: PMC8969249
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-022-00559-5
Analysis of lung cancer-related genetic changes in long-term and low-dose polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate (PHMG-p) treated human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Lung injury elicited by respiratory exposure to humidifier disinfectants (HDs) is known as HD-associated lung injury (HDLI). Current elucidation of the molecular mechanisms related to HDLI is mostly restricted to fibrotic and inflammatory lung diseases. In our previous report, we found that lung tumors were caused by intratracheal instillation of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate (PHMG-p) in a rat model. However, the lung cancer-related genetic changes concomitant with the development of these lung tumors have not yet been fully defined. We aimed to discover the effect of long-term exposure of PHMG-p on normal human lung alveolar cells.
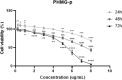
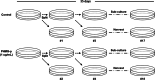
Methods: We investigated whether PHMG-p could increase distorted homeostasis of oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes, with long-term and low-dose treatment, in human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells (HPAEpiCs). Total RNA sequencing was performed with cells continuously treated with PHMG-p and harvested after 35 days.
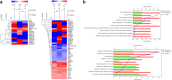
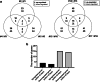
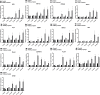
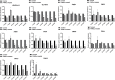
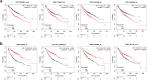
Results: After PHMG-p treatment, genes with transcriptional expression changes of more than 2.0-fold or less than 0.5-fold were identified. Within 10 days of exposure, 2 protein-coding and 5 non-coding genes were selected, whereas in the group treated for 27-35 days, 24 protein-coding and 5 non-coding genes were identified. Furthermore, in the long-term treatment group, 11 of the 15 upregulated genes and 9 of the 14 downregulated genes were reported as oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in lung cancer, respectively. We also found that 10 genes of the selected 24 protein-coding genes were clinically significant in lung adenocarcinoma patients.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that long-term exposure of human pulmonary normal alveolar cells to low-dose PHMG-p caused genetic changes, mainly in lung cancer-associated genes, in a time-dependent manner.
Keywords: Human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells; Humidifier disinfectant; Lung cancer related genes; Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate; Total RNA sequencing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Song JA, et al. Polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate induces severe lung inflammation, fibrosis, and thymic atrophy. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;69:267–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

