IL-27 Enhances γδ T Cell-Mediated Innate Resistance to Primary Hookworm Infection in the Lungs
- PMID: 35354611
- PMCID: PMC9012701
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000945
IL-27 Enhances γδ T Cell-Mediated Innate Resistance to Primary Hookworm Infection in the Lungs
Abstract
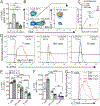
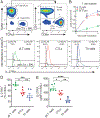
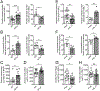
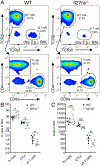
IL-27 is a heterodimeric IL-12 family cytokine formed by noncovalent association of the promiscuous EBI3 subunit and selective p28 subunit. IL-27 is produced by mononuclear phagocytes and unfolds pleiotropic immune-modulatory functions through ligation to IL-27 receptor α (IL-27RA). Although IL-27 is known to contribute to immunity and to limit inflammation after various infections, its relevance for host defense against multicellular parasites is still poorly defined. Here, we investigated the role of IL-27 during infection with the soil-transmitted hookworm, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, in its early host intrapulmonary life cycle. IL-27(p28) was detectable in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of C57BL/6J wild-type mice on day 1 after s.c. inoculation. IL-27RA expression was most abundant on lung-invading γδ T cells. Il27ra-/- mice showed increased lung parasite burden together with aggravated pulmonary hemorrhage and higher alveolar total protein leakage as a surrogate for epithelial-vascular barrier disruption. Conversely, injections of recombinant mouse (rm)IL-27 into wild-type mice reduced lung injury and parasite burden. In multiplex screens, higher airway accumulations of IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP-3 (CCL7) were observed in Il27ra-/- mice, whereas rmIL-27 treatment showed a reciprocal effect. Importantly, γδ T cell numbers in airways were enhanced by endogenous or administered IL-27. Further analysis revealed a direct antihelminthic function of IL-27 on γδ T cells as adoptive intratracheal transfer of rmIL-27-treated γδ T cells during primary N. brasiliensis lung infection conferred protection in mice. In summary, this report demonstrates protective functions of IL-27 to control the early lung larval stage of hookworm infection.
Copyright © 2022 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
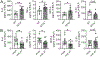

References
-
- Loukas A, Hotez PJ, Diemert D, Yazdanbakhsh M, McCarthy JS, Correa-Oliveira R, Croese J, and Bethony JM. 2016. Hookworm infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2: 16088. - PubMed
-
- Herricks JR, Hotez PJ, Wanga V, Coffeng LE, Haagsma JA, Basanez MG, Buckle G, Budke CM, Carabin H, Fevre EM, Furst T, Halasa YA, King CH, Murdoch ME, Ramaiah KD, Shepard DS, Stolk WA, Undurraga EA, Stanaway JD, Naghavi M, and Murray CJL. 2017. The global burden of disease study 2013: What does it mean for the NTDs? PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11: e0005424. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

