Simplified regimen for the management of hypertension with telemedicine and blood pressure self-monitoring (SIMPLE): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 35354637
- PMCID: PMC8968541
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049162
Simplified regimen for the management of hypertension with telemedicine and blood pressure self-monitoring (SIMPLE): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Telemedicine and blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring conduces to management of hypertension. Recent hypertension guidelines highly recommended single pill combination (SPC) for the initial treatment of essential hypertension. Based on this fact, an SPC-based telemedicine titration regimen with BP self-monitoring could be a better way in managing hypertension. This trial aims to elucidate whether telemedicine combined with BP self-monitoring is superior to self-monitoring alone during hypertension management.
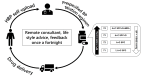
Methods and analysis: This study will be a multicentred, open-labelled, randomised controlled trial. A minimum sample of 358 hypertensive patients with uncontrolled BP from four centres will be included. The intervention group will include BP self-monitoring and tele-monitoring plus a free SPC-based telemedicine titration therapy for 6 months, they will be recommended to take BP measurements at least once every 7 days, in the meantime, researchers will call to give a consultation on lifestyle or titration advice once a fortnight. The control group will be required to self-monitor BP at the same time interval as intervention group, without any therapy change. Primary outcome of the trial will be the difference in systolic blood pressure at 6-month follow-up between intervention and control group, adjusted for baseline variables. Secondary outcomes such as BP control rate, major adverse cardiovascular events, medication adherence, quality of life will be investigated.
Ethics and dissemination: Ethics approval was granted by Ethical Committee of Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital (SHSY-IEC-4.1/20-194/01). The results will be disseminated in peer-reviewed literature, and to policy-makers and healthcare partners.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR2000037217.
Keywords: adult cardiology; epidemiology; hypertension.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
