Targeting Xist with compounds that disrupt RNA structure and X inactivation
- PMID: 35355011
- PMCID: PMC11549687
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04537-z
Targeting Xist with compounds that disrupt RNA structure and X inactivation
Abstract
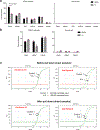
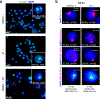
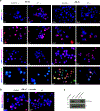
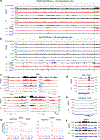
Although more than 98% of the human genome is non-coding1, nearly all of the drugs on the market target one of about 700 disease-related proteins. The historical reluctance to invest in non-coding RNA stems partly from requirements for drug targets to adopt a single stable conformation2. Most RNAs can adopt several conformations of similar stabilities. RNA structures also remain challenging to determine3. Nonetheless, an increasing number of diseases are now being attributed to non-coding RNA4 and the ability to target them would vastly expand the chemical space for drug development. Here we devise a screening strategy and identify small molecules that bind the non-coding RNA prototype Xist5. The X1 compound has drug-like properties and binds specifically the RepA motif6 of Xist in vitro and in vivo. Small-angle X-ray scattering analysis reveals that RepA can adopt multiple conformations but favours one structure in solution. X1 binding reduces the conformational space of RepA, displaces cognate interacting protein factors (PRC2 and SPEN), suppresses histone H3K27 trimethylation, and blocks initiation of X-chromosome inactivation. X1 inhibits cell differentiation and growth in a female-specific manner. Thus, RNA can be systematically targeted by drug-like compounds that disrupt RNA structure and epigenetic function.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures










Comment in
-
Small-molecule screens for targeting non-coding RNA.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022 May;21(5):338. doi: 10.1038/d41573-022-00064-8. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35393547 No abstract available.
-
The beginning of a new era: pioneering direct screens for RNA modulators.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jul 21;7(1):246. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01069-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35864086 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lee JT, Epigenetic regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Science 338 (6113), 1435–1439 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

