Profiling PI3K-AKT-MTOR variants in focal brain malformations reveals new insights for diagnostic care
- PMID: 35355055
- PMCID: PMC9630661
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awab376
Profiling PI3K-AKT-MTOR variants in focal brain malformations reveals new insights for diagnostic care
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Profiling PI3K-AKT-MTOR variants in focal brain malformations reveals new insights for diagnostic care.Brain. 2023 Jan 5;146(1):e7-e8. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac369. Brain. 2023. PMID: 36260430 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
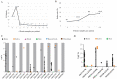
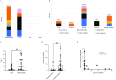
Focal malformations of cortical development including focal cortical dysplasia, hemimegalencephaly and megalencephaly, are a spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders associated with brain overgrowth, cellular and architectural dysplasia, intractable epilepsy, autism and intellectual disability. Importantly, focal cortical dysplasia is the most common cause of focal intractable paediatric epilepsy. Gain and loss of function variants in the PI3K-AKT-MTOR pathway have been identified in this spectrum, with variable levels of mosaicism and tissue distribution. In this study, we performed deep molecular profiling of common PI3K-AKT-MTOR pathway variants in surgically resected tissues using droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR), combined with analysis of key phenotype data. A total of 159 samples, including 124 brain tissue samples, were collected from 58 children with focal malformations of cortical development. We designed an ultra-sensitive and highly targeted molecular diagnostic panel using ddPCR for six mutational hotspots in three PI3K-AKT-MTOR pathway genes, namely PIK3CA (p.E542K, p.E545K, p.H1047R), AKT3 (p.E17K) and MTOR (p.S2215F, p.S2215Y). We quantified the level of mosaicism across all samples and correlated genotypes with key clinical, neuroimaging and histopathological data. Pathogenic variants were identified in 17 individuals, with an overall molecular solve rate of 29.31%. Variant allele fractions ranged from 0.14 to 22.67% across all mutation-positive samples. Our data show that pathogenic MTOR variants are mostly associated with focal cortical dysplasia, whereas pathogenic PIK3CA variants are more frequent in hemimegalencephaly. Further, the presence of one of these hotspot mutations correlated with earlier onset of epilepsy. However, levels of mosaicism did not correlate with the severity of the cortical malformation by neuroimaging or histopathology. Importantly, we could not identify these mutational hotspots in other types of surgically resected epileptic lesions (e.g. polymicrogyria or mesial temporal sclerosis) suggesting that PI3K-AKT-MTOR mutations are specifically causal in the focal cortical dysplasia-hemimegalencephaly spectrum. Finally, our data suggest that ultra-sensitive molecular profiling of the most common PI3K-AKT-MTOR mutations by targeted sequencing droplet digital polymerase chain reaction is an effective molecular approach for these disorders with a good diagnostic yield when paired with neuroimaging and histopathology.
Keywords: ddPCR; epilepsy; focal cortical dysplasia; hemimegalencephaly; mosaicism.
© The Author(s) (2022). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Guerrini R, Barba C. Focal cortical dysplasia: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Expert Rev Neurother. 2021;21(11):1213–1224. - PubMed
-
- Iffland PH2nd, Crino PB. Focal cortical dysplasia: Gene mutations, cell signaling, and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pathol. 2017;12:547–571. - PubMed
-
- Fauser S, Sisodiya SM, Martinian L, et al. Multi-focal occurrence of cortical dysplasia in epilepsy patients. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 8):2079–2090. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

