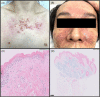
Dermatomyositis following COVID-19 vaccination
- PMID: 35355380
- PMCID: PMC9111860
- DOI: 10.1111/dth.15479
Dermatomyositis following COVID-19 vaccination
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

