Quantitative analysis of diaphragm motion during fluoroscopic sniff test to assist in diagnosis of hemidiaphragm paralysis
- PMID: 35355529
- PMCID: PMC8958460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.02.083
Quantitative analysis of diaphragm motion during fluoroscopic sniff test to assist in diagnosis of hemidiaphragm paralysis
Abstract
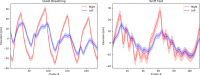
The current imaging gold standard for detecting paradoxical diaphragm motion and diagnosing hemidiaphragm paralysis is to perform the fluoroscopic sniff test. The images are visually examined by an experienced radiologist, and if one hemidiaphragm ascends while the other descends, then it is described as paradoxical motion, which is highly suggestive of hemidiaphragm paralysis. However, diagnosis can be challenging because diaphragm motion during sniffing is fast, paradoxical motion can be subtle, and the analysis is based on a 2-dimensional projection of a 3-dimensional surface. This paper presents a case of chronic left hemidiaphragm elevation that was initially reported as mild paradoxical motion on fluoroscopy. After measuring the elevations of the diaphragms and modeling their temporal correlation using Gaussian process regression, the systematic trend of the hemidiaphragmatic motion along with its stochastic properties was determined. When analyzing the trajectories of the hemidiaphragms, no statistically significant paradoxical motion was detected. This could potentially change the prognosis if the patient was to consider diaphragm plication as treatment. The presented method provides a more objective analysis of hemidiaphragm motions and can potentially improve diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: Diaphragm fluoroscopy; Diaphragm paralysis; Fluoroscopic sniff test; Gaussian process; Hemidiaphragm elevation; Machine learning.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures

References
-
- Tarver R, Conces D, Cory D, Vix V. Imaging the diaphragm and its disorders. J Thorac Imaging. 1989;4(1):1–18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

