Patellar Dislocation and Fracture After Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction in a Patient With Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- PMID: 35355651
- PMCID: PMC8929215
- DOI: 10.31486/toj.21.0025
Patellar Dislocation and Fracture After Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction in a Patient With Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Abstract
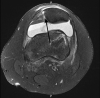
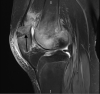
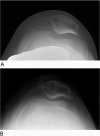
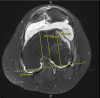
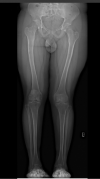
Background: Patellar instability is a common orthopedic condition in the pediatric population. Many factors contribute to patellar instability, including trochlear dysplasia. However, patellar instability and its treatments are not well documented in the literature for patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. Case Report: After medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) reconstruction, a 17-year-old male with osteogenesis imperfecta had a patellar dislocation that resulted in a patellar fracture. The patient subsequently had a revision of his MPFL reconstruction, and at 2½ years postoperation has had no episodes of recurrent patellar instability. Conclusion: The combination of bone fragility, trochlear dysplasia, and strength of the allograft used for MPFL reconstruction compared to the patient's bone strength led to dislocation and patellar fracture. Research into alternative methods for patellar fixation and postoperative physical therapy protocols for patients with osteogenesis imperfecta is needed. Special considerations must be made for this patient population.
Keywords: Osteogenesis imperfecta; patella; patellar dislocation; patellar ligament.
©2022 by the author(s); Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY).
Figures
References
-
- Hennrikus W, Pylawka T. Patellofemoral instability in skeletally immature athletes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(2):176-183. - PubMed
-
- Weeks KD 3rd, Fabricant PD, Ladenhauf HN, Green DW. Surgical options for patellar stabilization in the skeletally immature patient. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2012;20(3):194-202. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
