Deregulated expression and subcellular localization of CPSF6, a circRNA-binding protein, promote malignant development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35355934
- PMCID: PMC8913258
- DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2022.01.02
Deregulated expression and subcellular localization of CPSF6, a circRNA-binding protein, promote malignant development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Cleavage and polyadenylation specific factor 6 (CPSF6) has been documented as an oncoprotein in different types of cancer. However, functions of CPSF6 have not been investigated yet in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Here, we aimed to investigate the potential clinical values and biological functions of CPSF6 in ESCC.
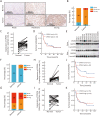
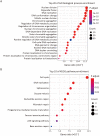
Methods: For determining the expression level of CPSF6 in ESCC patients, we analyzed published data, performed quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and immunohistochemistry assays. Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank tests were used for survival analyses. GO and KEGG analyses were done for CPSF6-related genes. Cell proliferation, colony formation and xenograft assays were conducted to verify the effects of CPSF6 on ESCC. In addition, cell cycle and apoptosis assays were also performed to manifest the functions of CPSF6 and circCPSF6. RNA pulldown and radioimmunoprecipitation (RIP) assays were used for confirming the interaction between circCPSF6 (hsa_circ_0000417) and CPSF6 protein. The regulatory relationship between CPSF6 protein and circCPSF6 was determined by RT-qPCR.
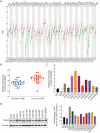
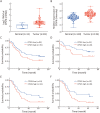
Results: We found that CPSF6 was upregulated in ESCC tissues and overexpression of cytoplasmic CPSF6 was associated with poor prognosis. GO and KEGG analyses suggested that CPSF6 could mainly affect cell division in ESCC. Further experiments manifested that CPSF6 promoted cell proliferation and colony formationin vitro. Xenograft assay showed that knockdown of CPSF6 significantly decreased tumor growth rate in vivo. Subsequently, we verified that depletion of CPSF6 led to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Finally, we validated that CPSF6, as a circRNA-binding protein, interacted with and regulated its circular isoform circCPSF6 (hsa_circ_0000417), of which depletion also resulted in cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in ESCC.
Conclusions: These findings gave us insight that overexpression of cytoplasmic CPSF6 protein is associated with poor prognosis in ESCC and CPSF6 may function as an oncoprotein, at least in part, through regulating circCPSF6 expression.
Keywords: CPSF6; cell proliferation; circCPSF6; circRNA-binding protein; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright ©2022 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: These authors have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000277 promotes tumor progression and DDP resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 4;22(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09241-9. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35241028 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000654 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulating the miR-149-5p/IL-6/STAT3 pathway.IUBMB Life. 2020 Mar;72(3):426-439. doi: 10.1002/iub.2202. Epub 2019 Nov 28. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 31778020
-
Circular RNA 0014715 Facilitates Cell Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Jun 15;13:4735-4749. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S314882. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34163248 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hsa_circ_0000711 expression level on proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Apr;24(8):4161-4171. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202004_20996. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32373952
-
Circular RNA circNTRK2 facilitates the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through up-regulating NRIP1 expression via miR-140-3p.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 11;39(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01640-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32653032 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
HIV-1-induced translocation of CPSF6 to biomolecular condensates.Trends Microbiol. 2024 Aug;32(8):781-790. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2024.01.001. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Trends Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38267295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of gene expression regulation by circRNA-protein interactions in cancer.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 17;8(1):77. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07383-z. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39825074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The possible molecular mechanism underlying the involvement of the variable shear factor QKI in the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of oesophageal cancer.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 10;18(7):e0288403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288403. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37428781 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of CPSF6 leads to global mRNA 3' UTR shortening and enhanced antiviral immune responses.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Feb 28;20(2):e1012061. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012061. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38416782 Free PMC article.
-
Current advances and future perspectives on the functional roles and clinical implications of circular RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: more influential than expected.Biomark Res. 2022 Jun 7;10(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00388-y. Biomark Res. 2022. PMID: 35672804 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
