Chest X-ray findings in drug-sensitive and drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis patients in Uganda
- PMID: 35355939
- PMCID: PMC8958542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2022.100312
Chest X-ray findings in drug-sensitive and drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis patients in Uganda
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Radiology has an important role in the diagnosis of both drug-sensitive (DS) and rifampicin-resistant (RR) pulmonary TB (PTB). This study aimed to compare the chest x-ray (CXR) patterns of microbiologically confirmed DS and RR PTB cases stratified by HIV serostatus in Uganda.
Methods: We conducted a hospital-based retrospective study at the Mulago National Referral Hospital (MNRH) TB wards. All participants had a microbiologically confirmed diagnosis of PTB. CXR findings extracted included infiltrates, consolidation, cavity, fibrosis, bronchiectasis, atelectasis, and other non-lung parenchymal findings. All films were examined by two independent radiologists blinded to the clinical diagnosis.
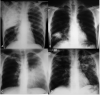
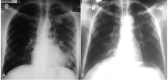
Results: We analyzed CXR findings of 165 participants: 139 DS- and 26 RR-TB cases. The majority (n = 118, 71.7%) of the participants were seronegative for HIV. Overall, 5/165 (3%) participants had normal CXR. There was no statistically significant difference in the proportion of participants with consolidations (74.8% versus 88.5%; p = 0.203), bronchopneumonic opacities (56.1% versus 42.3%, p = 0.207) and cavities (38.1% versus 46.2%, p = 0.514), across drug susceptibility status (DS versus RR TB). Among HIV-infected participants, consolidations were predominantly in the middle lung zone in the DS TB group and in the lower lung zone in the RR TB group (42.5% versus 12.8%, p = 0.66). HIV-infected participants with RR TB had statistically significantly larger cavity sizes compared to their HIV uninfected counterparts with RR TB (7.7 ± 6.8 cm versus 4.2 ± 1.3 cm, p = 0.004).
Conclusions: We observed that a vast majority of participants had similar CXR changes, irrespective of drug susceptibility status. However, HIV-infected RR PTB had larger cavities.The diagnostic utility of cavity sizes for the differentiation of HIV-infected and non-infected RR TB could be investigated further.
Keywords: Chest radiograph; DS-TB, Drug sensitive tuberculosis; Drug-sensitive; HIV, Human Immunodeficiency Virus; MDR, Multidrug resistant tuberculosis; MNRH, Mulago national referral hospital; MTB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; PTB, Pulmonary Tuberculosis; Pulmonary tuberculosis; RIF, Resistance to rifampicin; RR-TB, Rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis; Rifampicin-resistant; WHO, World Health Organization.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chest X-Ray Comparison Between Drug-Resistant and Drug-Sensitive Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children.Clin Respir J. 2024 Sep;18(9):e70010. doi: 10.1111/crj.70010. Clin Respir J. 2024. PMID: 39319395 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in pulmonary nodular consolidation and pulmonary cavity among drug-sensitive, rifampicin-resistant and multi-drug resistant tuberculosis patients: the Guangzhou computerized tomography study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):1010-1021. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-694. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38223080 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Xpert MTB/RIF on the treatment of multi-drug-resistant or rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis screened out from re-treatment pulmonary tuberculosis patients, a prospective cohort study.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 Mar;9(2):239-246. doi: 10.21037/apm.2020.02.17. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32233619
-
Imaging modalities for pulmonary tuberculosis in children: A systematic review.Eur J Radiol Open. 2022 Dec 30;10:100472. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2022.100472. eCollection 2023. Eur J Radiol Open. 2022. PMID: 36624819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Chest x-ray features and their associated factors among rifampicin/multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis patients in drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment initiating centers in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a retrospective study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Aug 2;25(1):974. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11344-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40753370 Free PMC article.
-
Chest X-Ray Comparison Between Drug-Resistant and Drug-Sensitive Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children.Clin Respir J. 2024 Sep;18(9):e70010. doi: 10.1111/crj.70010. Clin Respir J. 2024. PMID: 39319395 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in pulmonary nodular consolidation and pulmonary cavity among drug-sensitive, rifampicin-resistant and multi-drug resistant tuberculosis patients: a computerized tomography study with history length matched cases.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jul;14(7):2522-2531. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-145. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35928612 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in pulmonary nodular consolidation and pulmonary cavity among drug-sensitive, rifampicin-resistant and multi-drug resistant tuberculosis patients: the Guangzhou computerized tomography study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):1010-1021. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-694. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38223080 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal Chest X-Ray Findings of Patients With Confirmed Tuberculosis in Ghana.Cureus. 2025 Jun 19;17(6):e86359. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86359. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40688848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2020: executive summary [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020 [cited 2022 Mar 19]. 11 p. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/337538.
-
- Ubaidi BAA, Ubaidi BAA. The Radiological Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB) in Primary Care. [cited 2021 Aug 22]; Available from: https://clinmedjournals.org/articles/jfmdp/journal-of-family-medicine-an....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

