Association of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio With Plaque Rupture in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients With Only Intermediate Coronary Artery Lesions Assessed by Optical Coherence Tomography
- PMID: 35355959
- PMCID: PMC8960066
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.770760
Association of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio With Plaque Rupture in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients With Only Intermediate Coronary Artery Lesions Assessed by Optical Coherence Tomography
Abstract
Objectives: Plaque vulnerability and rupture rather than plaque size are the major cause of clinical events in patients with intermediate coronary lesions. Therefore, the present study was aimed to explore potential markers associated with plaque rupture in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients with intermediate coronary lesions.
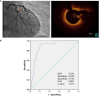
Methods: A total of 82 ACS patients presenting with only intermediate coronary lesions (40-70% stenosis demonstrated by quantitative coronary angiography) and no severe stenosis in other main coronary arteries [median age 63 years, 53 male and 29 female] were enrolled. Plaque morphology were assessed by optical coherence tomography (OCT). Hematological indices were assayed by automated hematological analyzer.
Results: Plaque rupture was identified in 14 patients by OCT. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in patients with plaque rupture (n = 14) was significantly higher than that in patients with non-plaque rupture (n = 68) [3.85 (3.28, 4.77) vs. 2.13 (1.40, 2.81), p < 0.001]. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that NLR was one of the independent risk factors for plaque rupture in intermediate coronary artery lesions (odds ratio 1.64, 95% confidence intervals 1.18-2.29, p = 0.003). ROC curve analysis found a cutoff point of NLR > 2.94 for plaque rupture with 93.8% sensitivity and 77.9% specificity.
Conclusion: NLR, an inflammatory biomarker, is closely associated with plaque rupture in intermediate coronary artery lesions. Monitoring NLR may be useful in risk stratification and management for intermediate coronary artery lesions.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; intermediate coronary artery lesion; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR); optical coherence tomography; plaque rupture.
Copyright © 2022 Jiang, Zeng, Zhuo, Wang, Gu, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio with Plaque Morphology in Patients with Asymptomatic Intermediate Carotid Artery Stenosis.Korean Circ J. 2016 Sep;46(5):699-705. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.5.699. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Korean Circ J. 2016. PMID: 27721862 Free PMC article.
-
Plaque rupture and intact fibrous cap assessed by optical coherence tomography portend different outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome.Eur Heart J. 2015 Jun 7;36(22):1377-84. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv029. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Eur Heart J. 2015. PMID: 25713314
-
Mean platelet volume and coronary plaque vulnerability: an optical coherence tomography study in patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019 May 29;19(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-1115-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019. PMID: 31142268 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of coronary plaques and atherosclerosis using optical coherence tomography.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2021 May;19(5):379-386. doi: 10.1080/14779072.2021.1914588. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2021. PMID: 33823735 Review.
-
[Intravascular ultrasound for recognition of atherosclerotic plaques and plaque composition. Current state of the diagnostic value].Herz. 2011 Aug;36(5):402-9. doi: 10.1007/s00059-011-3485-9. Herz. 2011. PMID: 21732096 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The association between neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and covert brain infarction after carotid endarterectomy: a single center retrospective study.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Mar 31;48(1):338. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03467-4. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40159523
-
Inflammation Biomarker-Driven Vertical Visualization Model for Predicting Long-Term Prognosis in Unstable Angina Pectoris Patients with Angiographically Intermediate Coronary Lesions.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Dec 6;17:10571-10584. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S497546. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39659751 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between the Platelet Lymphocyte Ratio and Albumin with Plaque Calcification in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: An Optical Coherence Tomography Study.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Apr 27;26(4):28167. doi: 10.31083/RCM28167. eCollection 2025 Apr. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40351665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, Bailey SR, Bittl JA, Cercek B, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI guideline for percutaneous coronary intervention: executive summary: a report of the American college of cardiology foundation/American heart association task force on practice guidelines and the society for cardiovascular angiography and interventions. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2012) 79:453–95. 10.1002/ccd.23438 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

