Effects of Gut Microbiota on Host Adaptive Immunity Under Immune Homeostasis and Tumor Pathology State
- PMID: 35355998
- PMCID: PMC8960063
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.844335
Effects of Gut Microbiota on Host Adaptive Immunity Under Immune Homeostasis and Tumor Pathology State
Abstract
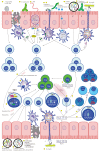
Gut microbiota stimulate and shape the body's adaptive immune response through bacterial components and its active metabolites, which orchestrates the formation and maintenance of the body's immune homeostasis. In addition, the imbalances in microbiota-adaptive immunity contribute to the development of tumor and the antitumor efficiency of a series of antitumor therapies at the preclinical and clinical levels. Regardless of significant results, the regulation of gut microbiota on adaptive immunity in immune homeostasis and tumors needs a more thorough understanding. Herein, we highlighted the comprehensive knowledge, status, and limitations in the mechanism of microbiome interaction with adaptive immunity and put forward the prospect of how to translate these insights in inhibiting tumor progression and enhancing the efficacy of antitumor interventions.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; homeostasis; immunotherapy; microbiota; tumor.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Ye, Zhu, Fang, Meng and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
JZ and SF were employed by Wecare Probiotics Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

