Recent advance in treatment of atherosclerosis: Key targets and plaque-positioned delivery strategies
- PMID: 35356091
- PMCID: PMC8958685
- DOI: 10.1177/20417314221088509
Recent advance in treatment of atherosclerosis: Key targets and plaque-positioned delivery strategies
Abstract
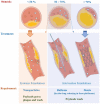
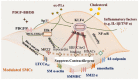
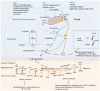
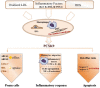
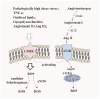
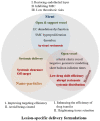
Atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease of vascular wall, is a progressive pathophysiological process with lipids oxidation/depositing initiation and innate/adaptive immune responses. The coordination of multi systems covering oxidative stress, dysfunctional endothelium, diseased lipid uptake, cell apoptosis, thrombotic and pro-inflammatory responding as well as switched SMCs contributes to plaque growth. In this circumstance, inevitably, targeting these processes is considered to be effective for treating atherosclerosis. Arriving, retention and working of payload candidates mediated by targets in lesion direct ultimate therapeutic outcomes. Accumulating a series of scientific studies and clinical practice in the past decades, lesion homing delivery strategies including stent/balloon/nanoparticle-based transportation worked as the potent promotor to ensure a therapeutic effect. The objective of this review is to achieve a very brief summary about the effective therapeutic methods cooperating specifical targets and positioning-delivery strategies in atherosclerosis for better outcomes.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; balloon; nanoparticle; site-homing delivery; stent; targets.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Liu Y, Chen BPC, Lu M, et al.. Shear stress activation of SREBP1 in endothelial cells is mediated by integrins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2002; 22: 76–81. - PubMed
-
- Gu L, Okada Y, Clinton SK, et al.. Absence of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 reduces atherosclerosis in low density lipoprotein receptor–deficient mice. Mol Cell 1998; 2: 275–281. - PubMed
-
- Steinberg D. Low density lipoprotein oxidation and its pathobiological significance. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 20963–20966. - PubMed
-
- Hossain E, Ota A, Karnan S, et al.. Lipopolysaccharide augments the uptake of oxidized LDL by up-regulating lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 in macrophages. Mol Cell Biochem 2015; 400: 29–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

