Translocator Protein (TSPO) Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Activating Spinal Autophagy and Nuclear SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling in a Rat L5 SNL Model
- PMID: 35356265
- PMCID: PMC8959876
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S359397
Translocator Protein (TSPO) Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Activating Spinal Autophagy and Nuclear SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling in a Rat L5 SNL Model
Abstract
Purpose: Recent studies showed promotion of astrocyte autophagy in the spinal cord would provide analgesic effects. Silent information regulator T1 (SIRT1) and α subunit of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1 (PGC-1α) are two master regulators of endogenous antioxidant defense and mitochondrial biogenesis. They play vital roles in both autophagy and neuropathic pain (NP). Our previous study showed that TSPO agonist Ro5-4864 elicited potent analgesic effects against NP, but the mechanisms remain unclear. This study aims to investigate the effects of TSPO agonist Ro5-4864 on autophagy and nuclear SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling in spinal dorsal horn.
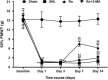
Methods: A rat model of L5 spinal nerve ligation (SNL) was adopted. Rats were randomly assigned to the Sham group, the SNL group, the Ro (TSPO agonist Ro5-4864) group and the Ro+3-MA group. The behavior assessments were conducted at baseline, on Day 1, 3, 7 and 14 after SNL. The autophagy-related proteins (ATG7, Beclin1, LC3, and P62) in spinal dorsal horn were assayed and the nuclear SIRT1/PGC-1α and downstream factors were analyzed.
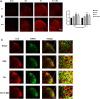
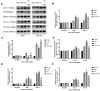
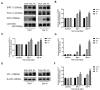
Results: Ro5-4864 alleviated the mechanical allodynia induced by SNL (P < 0.01 vs the SNL group), which could be totally abrogated by autophagy inhibitor 3-MA (P < 0.01 vs the Ro group). SNL induced elevated ATG7 (P < 0.01), Beclin1 (P < 0.01) and LC3-II/LC3-I (P < 0.01) contents and P62 accumulation (P < 0.01) on Day 7 and Day 14, which suggested an autophagy flux impairment. Ro5-4864 augmented ATG7 (P < 0.01), Beclin1 (P < 0.01) and LC3-II/LC3-I (P < 0.05) with decreased P62 (P < 0.01), which indicated a more fluent autophagic process. These effects were also totally abrogated by 3-MA (P < 0.01). Furthermore, Ro5-4864 activated the spinal nuclear SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway.
Conclusion: TSPO improved both autophagy impairment and mitochondrial biogenesis, which may provide a new strategy for the treatment of NP.
Keywords: PGC-1α; SIRT1; TSPO; autophagy; neuropathic pain; silent information regulator T1; translocator protein; α subunit of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1.
© 2022 Hao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Can Hao and Bingjie Ma are co-first authors for this study. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

