Global Survey, Expressions and Association Analysis of CBLL Genes in Peanut
- PMID: 35356435
- PMCID: PMC8959419
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.821163
Global Survey, Expressions and Association Analysis of CBLL Genes in Peanut
Abstract
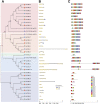
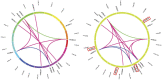
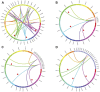
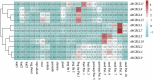
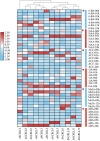
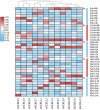
Cystathionine γ-synthase (CGS), methionine γ-lyase (MGL), cystathionine β-lyase (CBL) and cystathionine γ-lyase (CGL) share the Cys_Met_Meta_PP domain and play important roles in plant stress response and development. In this study, we defined the genes containing the Cys_Met_Meta_PP domain (PF01053.20) as CBL-like genes (CBLL). Twenty-nine CBLL genes were identified in the peanut genome, including 12 from cultivated peanut and 17 from wild species. These genes were distributed unevenly at the ends of different chromosomes. Evolution, gene structure, and motif analysis revealed that CBLL proteins were composed of five different evolutionary branches. Chromosome distribution pattern and synteny analysis strongly indicated that whole-genome duplication (allopolyploidization) contributed to the expansion of CBLL genes. Comparative genomics analysis showed that there were three common collinear CBLL gene pairs among peanut, Arabidopsis, grape, and soybean, but no collinear CBLL gene pairs between peanut and rice. The prediction results of cis-acting elements showed that AhCBLLs, AdCBLLs, and AiCBLLs contained different proportions of plant growth, abiotic stress, plant hormones, and light response elements. Spatial expression profiles revealed that almost all AhCBLLs had significantly higher expression in pods and seeds. All AhCBLLs could respond to heat stress, and some of them could be rapidly induced by cold, salt, submergence, heat and drought stress. Furthermore, one polymorphic site in AiCBLL7 was identified by association analysis which was closely associated with pod length (PL), pod width (PW), hundred pod weight (HPW) and hundred seed weight (HSW). The results of this study provide a foundation for further research on the function of the CBLL gene family in peanut.
Keywords: CBLL gene family; cis-acting element; expression pattern; genome-wide association analysis; peanut.
Copyright © 2022 Ren, Zeng, Wang, Zhang, Fang and Wan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

