Research progress of aldehyde oxidases in plants
- PMID: 35356472
- PMCID: PMC8958963
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13119
Research progress of aldehyde oxidases in plants
Abstract
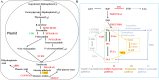
Plant aldehyde oxidases (AOs) are multi-functional enzymes, and they could oxidize abscisic aldehyde into ABA (abscisic acid) or indole acetaldehyde into IAA (indoleacetic acid) as the last step, respectively. AOs can be divided into four groups based on their biochemical and physiological functions. In this review, we summarized the recent studies about AOs in plants including the motif information, biochemical, and physiological functions. Besides their role in phytohormones biosynthesis and stress response, AOs could also involve in reactive oxygen species homeostasis, aldehyde detoxification and stress tolerance.
Keywords: Abscisic acid; Aldehyde oxidases; Indoleacetic acid; Stress.
© 2022 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Akaba S, Seo M, Dohmae N, Takio K, Sekimoto H, Kamiya Y, Furuya N, Romano T, Koshiba T. Production of homo- and hetero-dimeric isozymes from two aldehyde oxidase genes of Arabidopsis thaliana. The Journal of Biochemistry. 1999;126(2):395–401. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022463. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Audran C, Liotenberg S, Gonneau M, North H, Frey A, Tap-Waksman K, Vartanian N, Marion-Poll A. Localisation and expression of zeaxanthin epoxidase mRNA in Arabidopsis in response to drought stress and during seed development. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology. 2001;28(12):1161–1173. doi: 10.1071/pp00134. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

