The Hemophilia Joint Health Score version 2.1 Validation in Adult Patients Study: A multicenter international study
- PMID: 35356667
- PMCID: PMC8956786
- DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12690
The Hemophilia Joint Health Score version 2.1 Validation in Adult Patients Study: A multicenter international study
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022 Apr 25;6(3):e12713. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12713. eCollection 2022 Mar. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 35494507 Free PMC article.
-
Corrigendum to 'The Hemophilia Joint Health Score version 2.1 Validation in Adult Patients Study: A multicenter international study' [Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 6/2, (2022) e12690].Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023 Apr 27;7(3):100157. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.100157. eCollection 2023 Mar. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 37275180 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The Hemophilia Joint Health Score (HJHS) was developed and validated to detect arthropathy in children. Additional evidence is required to show validity in adults. We studied the convergent and discriminant construct validity of the HJHS version 2.1(HJHSv2.1) in adults with hemophilia. A secondary aim was to define age-related normative adult HJHSv2.1 reference values.
Methods: We studied 192 adults with hemophilia, and 120 healthy adults in four age-matched groups-18 to 29, 30 to 40, 41 to 50, and >50 years-at nine centers. Trained physiotherapists scored the HJHS and World Federation of Hemophilia (WFH) joint score. Health history, the Functional Independence Scale of Hemophilia (FISH), Hemophilia Activities List (HAL), and Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ) were also collected.
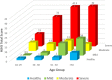
Results: The median age was 35.0 years. Of participants with hemophilia, 68% had severe, 14% moderate, and 18% mild disease. The HJHS correlated strongly with WFH score (Spearman's rho [rs ] = .95, P < .001). Moderate correlations were seen between the FISH (rs = .50, P < .001) and SF-MPQ Present Pain Intensity (rs = .50, P < .001), while a modest correlation was found with the HAL (rs = -.37, P < .001). The HJHS significantly differentiated between age groups (Kruskal-Wallis T = 35.02, P < .001) and disease severity in participants with hemophilia. The HJHS had high internal reliability (Cronbach's α = .88). We identified duration of swelling as a redundant item in the HJHS.
Conclusions: The HJHS shows evidence of strong convergent and discriminant construct validity to detect arthropathy in adults with hemophilia and is well suited for use in this population.
Keywords: adult; arthropathy; hemarthrosis; hemophilia; validity of results.
© 2022 The Authors. Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH).
Figures
References
-
- Valentino LA. Blood‐induced joint disease: the pathophysiology of hemophilic arthropathy. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8:1895‐1902. - PubMed
-
- Oldenburg J. Optimal treatment strategies for hemophilia: achievements and limitations of current prophylactic regimens. Blood. 2015;125:2038‐2044. - PubMed
-
- Fischer K, Poonnoose P, Dunn AL, et al. Choosing outcome assessment tools in haemophilia care and research: a multidisciplinary perspective. Haemophilia. 2017;23(1):11‐24. - PubMed
-
- Kuijlaars IAR, Timmer MA, de Kleijn P, Pisters MF, Fischer K. Monitoring joint health in haemophilia: factors associated with deterioration. Haemophilia. 2017;23:934‐940. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources