Comparing the efficacy and safety of short-term spinal cord stimulation and pulsed radiofrequency for zoster-related pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35356934
- PMCID: PMC10684147
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029073
Comparing the efficacy and safety of short-term spinal cord stimulation and pulsed radiofrequency for zoster-related pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) is a commonly used method for the treatment of zoster-related pain in the clinic. However, PRF therapy has a high recurrence rate and many adverse reactions. Recent studies have shown that short-term spinal cord stimulation (stSCS) can effectively alleviate zoster-related pain. Due to the lack of evidence, it is unclear whether stSCS is superior to PRF in the efficacy of treating zoster-related pain.
Objective: This study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of stSCS and PRF for zoster-related pain.
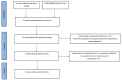
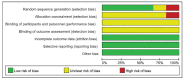
Methods: We searched seven electronic databases from the establishment of the database to January 2021. Related randomized controlled trials were included in this meta-analysis. After extracting the data and evaluating the methodological quality of the included trials, the outcome indicators were statistically analyzed by using RevManV.5.3.
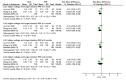
Results: This meta-analysis included 6 trials with a total of 509 patients. Compared with PRF group, stSCS group showed lower pain intensity (standardized mean difference=-0.83, 95%CI [-1.37, -0.30], P=.002), better sleep quality (mean difference=-1.43, 95%CI [-2.29, -0.57], P=.001), lower pain rating index scores, and less incidence of adverse events (RR=0.32, 95%CI [0.12, 0.83], P<.05). However, the efficacies of PRF and stSCS for treating postherpetic neuralgia were consistent in the response rate (RR= 1.10, 95% CI [0.82, 1.48], P=.51) and the complete remission rate (RR=1.05, 95% CI [0.66, 1.68], P=.84).
Conclusions: In this study, stSCS showed a better analgesic effect and higher safety than PRF. Our meta-analysis results suggested that stSCS may be a feasible and safe invasive treatment for zoster-related pain. However, high-quality, randomized controlled trials with large sample sizes are needed to further verify our conclusions.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures





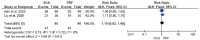
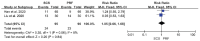
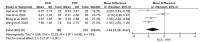
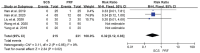
References
-
- Schmader K. Herpes zoster. Ann Intern Med 2018;169:ITC19- 31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

