Digital Light Processing Bioprinting Advances for Microtissue Models
- PMID: 35357144
- PMCID: PMC10700125
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c01509
Digital Light Processing Bioprinting Advances for Microtissue Models
Abstract
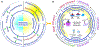
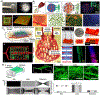
Digital light processing (DLP) bioprinting has been widely introduced as a fast and robust biofabrication method in tissue engineering. The technique holds a great promise for creating tissue models because it can replicate the resolution and complexity of natural tissues and constructs. A DLP system projects 2D images onto layers of bioink using a digital photomask. The resolution of DLP bioprinting strongly depends on the characteristics of the projected light and the photo-cross-linking response of the bioink microenvironment. In this review, we present a summary of DLP fundamentals with a focus on bioink properties, photoinitiator selection, and light characteristics in resolution of bioprinted constructs. A simple guideline is provided for bioengineers interested in using DLP platforms and customizing technical specifications for its design. The literature review reveals the promising future of DLP bioprinting for disease modeling and biofabrication.
Keywords: bioprinter design; digital light processing; tissue engineering; vascularized models.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare no Conflict of Interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bhatia SN; Ingber DE Microfluidic Organs-on-Chips. Nat. Biotechnol 2014, 32 (8), 760–772. - PubMed
-
- Kuo C. Te; Chiang CL; Huang RYJ; Lee H; Wo AM Configurable 2D and 3D Spheroid Tissue Cultures on Bioengineered Surfaces with Acquisition of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Characteristics. NPG Asia Mater. 2012, 4 (9), 1–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
