Accessory Genomes Drive Independent Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Groups 258 and 307 in Houston, TX
- PMID: 35357213
- PMCID: PMC9040855
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.00497-22
Accessory Genomes Drive Independent Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Groups 258 and 307 in Houston, TX
Abstract
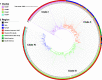
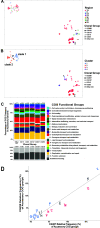
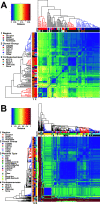
Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKp) is an urgent public health threat. Worldwide dissemination of CRKp has been largely attributed to clonal group (CG) 258. However, recent evidence indicates the global emergence of a CRKp CG307 lineage. Houston, TX, is the first large city in the United States with detected cocirculation of both CRKp CG307 and CG258. We sought to characterize the genomic and clinical factors contributing to the parallel endemic spread of CG258 and CG307. CRKp isolates were collected as part of the prospective, Consortium on Resistance against Carbapenems in Klebsiella and other Enterobacterales 2 (CRACKLE-2) study. Hybrid short-read and long-read genome assemblies were generated from 119 CRKp isolates (95 originated from Houston hospitals). A comprehensive characterization of phylogenies, gene transfer, and plasmid content with pan-genome analysis was performed on all CRKp isolates. Plasmid mating experiments were performed with CG307 and CG258 isolates of interest. Dissection of the accessory genomes suggested independent evolution and limited horizontal gene transfer between CG307 and CG258 lineages. CG307 contained a diverse repertoire of mobile genetic elements, which were shared with other non-CG258 K. pneumoniae isolates. Three unique clades of Houston CG307 isolates clustered distinctly from other global CG307 isolates, indicating potential selective adaptation of particular CG307 lineages to their respective geographical niches. CG307 strains were often isolated from the urine of hospitalized patients, likely serving as important reservoirs for genes encoding carbapenemases and extended-spectrum β-lactamases. Our findings suggest parallel cocirculation of high-risk lineages with potentially divergent evolution. IMPORTANCE The prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKp) infections in nosocomial settings remains a public health challenge. High-risk clones such as clonal group 258 (CG258) are particularly concerning due to their association with blaKPC carriage, which can severely complicate antimicrobial treatments. There is a recent emergence of clonal group 307 (CG307) worldwide with little understanding of how this successful clone has been able to adapt while cocirculating with CG258. We provide the first evidence of potentially divergent evolution between CG258 and CG307 with limited sharing of adaptive genes. Houston, TX, is home to the largest medical center in the world, with a large influx of domestic and international patients. Thus, our unique geographical setting, where two pandemic strains of CRKp are circulating, provides an indication of how differential accessory genome content can drive stable, endemic populations of CRKp. Pan-genomic analyses such as these can reveal unique signatures of successful CRKp dissemination, such as the CG307-associated plasmid (pCG307_HTX), and provide invaluable insights into the surveillance of local carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) epidemiology.
Keywords: CG258; CG307; carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae; divergent evolution; genomic surveillance; mobile genetic elements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a conflict of interest. CAA reports Grants from NIH, Merck, Memed Diagnostics and Entasis pharmaceuticals. Royalties from UpToDate, and editor's stipend from American Society for Microbiology. VGF reports personal consultancy fees from Novartis, Novadigm, Durata, Debiopharm, Genentech, Achaogen, Affinium, Medicines Co., Cerexa, Tetraphase, Trius, MedImmune, Bayer, Theravance, Basilea, Affinergy, Janssen, xBiotech, Contrafect, Regeneron, Basilea, Destiny, Amphliphi Biosciences. Integrated Biotherapeutics; C3J, Armata, Valanbio; Akagera, Aridis; Grants from NIH, MedImmune, Allergan, Pfizer, Advanced Liquid Logics, Theravance, Novartis, Merck; Medical Biosurfaces; Locus; Affinergy; Contrafect; Karius; Genentech, Regeneron, Basilea, Janssen, Royalties from UpToDate; Stock options Valanbio; a patent pending in sepsis diagnostics; educational fees from Green Cross, Cubist, Cerexa, Durata, Theravance, and Debiopharm; and an editor's stipend from IDSA.
Figures


References
-
- Yigit H, Queenan AM, Anderson GJ, Domenech-Sanchez A, Biddle JW, Steward CD, Alberti S, Bush K, Tenover FC. 2001. Novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase, KPC-1, from a carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:1151–1161. doi:10.1128/AAC.45.4.1151-1161.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Duin D, Arias CA, Komarow L, Chen L, Hanson BM, Weston G, Cober E, Garner OB, Jacob JT, Satlin MJ, Fries BC, Garcia-Diaz J, Doi Y, Dhar S, Kaye KS, Earley M, Hujer AM, Hujer KM, Domitrovic TN, Shropshire WC, Dinh A, Manca C, Luterbach CL, Wang M, Paterson DL, Banerjee R, Patel R, Evans S, Hill C, Arias R, Chambers HF, Fowler VG, Kreiswirth BN, Bonomo RA, Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Network Investigators . 2020. Molecular and clinical epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in the USA (CRACKLE-2): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 20:731–741. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30755-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

