O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor ASN90 is a Multimodal Drug Candidate for Tau and α-Synuclein Proteinopathies
- PMID: 35357812
- PMCID: PMC9026285
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00057
O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor ASN90 is a Multimodal Drug Candidate for Tau and α-Synuclein Proteinopathies
Abstract
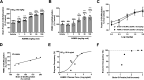
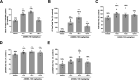
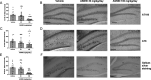
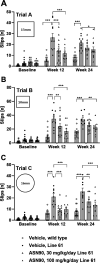
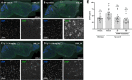
Neurodegenerative proteinopathies are characterized by the intracellular formation of insoluble and toxic protein aggregates in the brain that are closely linked to disease progression. In Alzheimer's disease and in rare tauopathies, aggregation of the microtubule-associated tau protein leads to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles (NFT). In Parkinson's disease (PD) and other α-synucleinopathies, intracellular Lewy bodies containing aggregates of α-synuclein constitute the pathological hallmark. Inhibition of the glycoside hydrolase O-GlcNAcase (OGA) prevents the removal of O-linked N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (O-GlcNAc) moieties from intracellular proteins and has emerged as an attractive therapeutic approach to prevent the formation of tau pathology. Like tau, α-synuclein is known to be modified with O-GlcNAc moieties and in vitro these have been shown to prevent its aggregation and toxicity. Here, we report the preclinical discovery and development of a novel small molecule OGA inhibitor, ASN90. Consistent with the substantial exposure of the drug and demonstrating target engagement in the brain, the clinical OGA inhibitor ASN90 promoted the O-GlcNAcylation of tau and α-synuclein in brains of transgenic mice after daily oral dosing. Across human tauopathy mouse models, oral administration of ASN90 prevented the development of tau pathology (NFT formation), functional deficits in motor behavior and breathing, and increased survival. In addition, ASN90 slowed the progression of motor impairment and reduced astrogliosis in a frequently utilized α-synuclein-dependent preclinical rodent model of PD. These findings provide a strong rationale for the development of OGA inhibitors as disease-modifying agents in both tauopathies and α-synucleinopathies. Since tau and α-synuclein pathologies frequently co-exist in neurodegenerative diseases, OGA inhibitors represent unique, multimodal drug candidates for further clinical development.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; O-GlcNAcase inhibitor; Parkinson’s disease; drug development; microtubule-associated protein tau; proteinopathies; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): All authors are or were employees of Asceneuron and hold shares, founder warrants or stock options of the company.
Figures
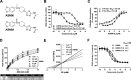


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of O-GlcNAcase leads to elevation of O-GlcNAc tau and reduction of tauopathy and cerebrospinal fluid tau in rTg4510 mice.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 May 18;12(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0181-0. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28521765 Free PMC article.
-
MK-8719, a Novel and Selective O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor That Reduces the Formation of Pathological Tau and Ameliorates Neurodegeneration in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020 Aug;374(2):252-263. doi: 10.1124/jpet.120.266122. Epub 2020 Jun 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020. PMID: 32493725
-
Hyperphosphorylated Tau in an α-synuclein-overexpressing transgenic model of Parkinson's disease.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 May;33(9):1598-610. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07660.x. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21453448 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between APOE Variants, Tau and α-Synuclein.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1184:177-186. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9358-8_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 32096038 Review.
-
O-GlcNAcase inhibitors as potential therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and related tauopathies: analysis of the patent literature.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2021 Dec;31(12):1117-1154. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2021.1947242. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2021. PMID: 34176417 Review.
Cited by
-
O-GlcNAcylation regulates neurofilament-light assembly and function and is perturbed by Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease mutations.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 17;14(1):6558. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42227-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37848414 Free PMC article.
-
An Efficient and Accessible Hectogram-Scale Synthesis for the Selective O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor Thiamet-G.ACS Omega. 2024 Dec 8;9(50):49223-49228. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c06141. eCollection 2024 Dec 17. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39713709 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Transcriptome Changes Associated With an Acute Increase of Protein O-GlcNAcylation and Implications for Neurodegenerative Disease.J Neurochem. 2025 Jan;169(1):e16302. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16302. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 39823370 Free PMC article.
-
Top/Middle-Down Characterization of α-Synuclein Glycoforms.Anal Chem. 2023 Dec 12;95(49):18039-18045. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02405. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 38047498 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization Analysis of Tau Protein in the Brain of Alzheimer's Disease: A Scoping Literature Review.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024;21(9):649-666. doi: 10.2174/0115672050351995241223065923. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024. PMID: 39902543
References
-
- Sánchez R. G.; Parrish R. R.; Rich M.; Webb W. M.; Lockhart R. M.; Nakao K.; Ianov L.; Buckingham S. C.; Broadwater D. R.; Jenkins A.; de Lanerolle N. C.; Cunningham M.; Eid T.; Riley K.; Lubin F. D. Human and rodent temporal lobe epilepsy is characterized by changes in O-GlcNAc homeostasis that can be reversed to dampen epileptiform activity. Neurobiol Dis 2019, 124, 531–543. 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.01.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

