Segmental duplications and their variation in a complete human genome
- PMID: 35357917
- PMCID: PMC8979283
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abj6965
Segmental duplications and their variation in a complete human genome
Abstract
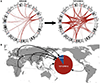
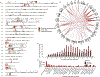
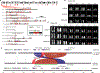
Despite their importance in disease and evolution, highly identical segmental duplications (SDs) are among the last regions of the human reference genome (GRCh38) to be fully sequenced. Using a complete telomere-to-telomere human genome (T2T-CHM13), we present a comprehensive view of human SD organization. SDs account for nearly one-third of the additional sequence, increasing the genome-wide estimate from 5.4 to 7.0% [218 million base pairs (Mbp)]. An analysis of 268 human genomes shows that 91% of the previously unresolved T2T-CHM13 SD sequence (68.3 Mbp) better represents human copy number variation. Comparing long-read assemblies from human (n = 12) and nonhuman primate (n = 5) genomes, we systematically reconstruct the evolution and structural haplotype diversity of biomedically relevant and duplicated genes. This analysis reveals patterns of structural heterozygosity and evolutionary differences in SD organization between humans and other primates.
Figures


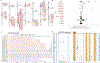
Comment in
-
The final pieces of the human genome.Nat Rev Genet. 2022 Jun;23(6):321. doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00494-5. Nat Rev Genet. 2022. PMID: 35488041 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ohno Wolf, Atkin, Evolution from fish to mammals by gene duplication. Hereditas. 59, 169–187 (1968). - PubMed
-
- Ohno, Evolution by Gene Duplication (Springer Science & Business Media, 1970).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

