The eight-year long-term follow-up on the effectiveness of the quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine in Chinese women 20-45 years of age
- PMID: 35358015
- PMCID: PMC9225595
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2052700
The eight-year long-term follow-up on the effectiveness of the quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine in Chinese women 20-45 years of age
Abstract
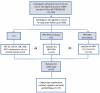
The quadrivalent human papillomavirus (4vHPV) vaccine has shown confirmative effectiveness in preventing HPV-related diseases among women and men around the globe. The phase III, randomized, double-blind efficacy study (Base study, NCT00834106) conducted in China showed 100% efficacy against HPV 16/18-related cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and efficacy against HPV persistent infection for 78 months. Participants aged 20-45 years who received three doses of 4vHPV vaccine or placebo during the base study were selected and invited for this long-term follow-up (LTFU) study to assess the long-term effectiveness of the 4vHPV vaccine in preventing HPV-related diseases. A total of 368 participants were included in this LTFU study with a median follow-up of 94 months. Among 27 participants (Vaccine vs. Placebo: 8 vs. 19) who underwent colposcopy and biopsy due to cervical cytological abnormalities or HPV infection, no HPV-16/18-related cases of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), or vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VaIN) was observed in the vaccine group while two HPV-16-related cases (CIN1/VaIN) were observed in the placebo group. There were another two HPV-related cases (non-vaccine HPV types) found in the placebo group. Consistent with the findings from global studies that suggested long-term efficacy of 4vHPV vaccine, our study showed continued protective effect of 4vHPV vaccine against HPV-related precancerous diseases through a median follow-up time of 94 months with the longest follow-up time of 125 months after completing three doses of vaccination among Chinese women 20-45 years of age.
Keywords: Human papillomavirus vaccine; effectiveness; long-term follow-up.
Conflict of interest statement
Chao Zhao, Yun Zhao, Jingran Li, Mingzhu Li, Danhua Shen, and Lihui Wei have received grants/research support from MSD R&D (China).
Figures
References
-
- Food and Drug Administration . Summary basis for regulatory action - Gardasil 9. 2018. [accessed 2021 Sep 1]. https://www.fda.gov/media/117054/download.
-
- European Medicines Agency . Gardasil 9 - Human papillomavirus 9-valent vaccine (recombinant, adsorbed) (EMA/192711/2016). 2016. [accessed 2021 Sep 1]. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/overview/gardasil-9-epar-summary-....
-
- Chinese vaccine for HPV approved. 2020. [accessed 2021 Sep 1]. https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202001/02/WS5e0d4067a310cf3e35581efd.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources